Abstract on the topic of edible mushrooms in nature. Edible and Poisonous Mushrooms
Many mushrooms are consumed by people as a tasty and nutritious product. The fruit bodies of mushrooms have a lot of water and a wide range of organic and mineral substances. Most of the dry matter of mushrooms is made up of proteins and nitrogenous compounds, including fungal fiber. The basis of this nitrogen-containing polysaccharide is fungin (mycetin), a substance similar to chitin, which consists of the covers of insects and shells of crustaceans. Naturally, mushroom fiber is difficult to digest, which somewhat reduces the nutritional value of mushrooms.
The abundance of proteins in mushrooms explains not only their common name - forest meat, but also the method of use: mushrooms are really used instead of meat, and not as a substitute for vegetables. Carbohydrates in mushrooms are approximately two times less than proteins, and this differs from green plants, which are characterized by an inverse ratio. An essential feature of the carbohydrate composition of macromycetes is the presence of specific fungal sugar of mycosis and the complete absence of starch, instead of which glycogen accumulates in the fungal cells.
Edible mushrooms are rich in vitamins. Vitamins A, B1, B2, C, D, and PP were found in their fruiting bodies. Vitamin A is especially abundant in chanterelles and mushrooms; here it is represented by carotene (provitamin A), which stains these mushrooms in a bright color. By the content of thiamine (vitamin B1), many mushrooms are not inferior to grain products. Nicotinic acid (vitamin PP) in mushrooms is about as much as in the liver.
By the presence of minerals, mushrooms approach fruit. The composition of mushroom cells includes salts of potassium, phosphorus (almost as much as in fish), sodium, calcium, iron. Mushrooms contain zinc, copper, fluorine and other trace elements, however, they are not higher than the norm common for plant products.
Studies of the biochemical composition of mushrooms have shown that many of them are sources of biologically active and medicinal substances. It is known that some mushrooms are used in folk medicine. To date, more than 40 biologically active substances contained in mushrooms have been isolated.

Edible mushrooms. From left to right: porcini, marsh boletus, white dung beetle, autumn honey agaric, Russula
Some edible mushrooms (for example, champignons) are bred in abandoned mines and caves, cellars and sheds.
However, among macromycetes a number of poisonous and not edible mushroomscapable of causing poisoning. These are, first of all, fly agarics and grebes, false mushrooms, etc. There are no reliable methods to distinguish edible and poisonous mushrooms; often they are part of the same family, so you should collect only those mushrooms in which you are sure. Most edible and poisonous mushrooms belong to marsupials and basidiomycetes.

Poisonous mushrooms. From left to right: death cap, red fly agaric, gray-yellow false honey fly, waxy talker, thin pig
Conditionally edible mushrooms can also cause poisoning - morels and stitches, undigested sows, unsalted waves, whites and other mushrooms with a pungent taste. Overgrown fruiting bodies, in which decay products have accumulated, can also serve as a cause of poisoning. Fungal poison is dangerous in that its effect appears only 12-24 hours after poisoning, when it is almost impossible to neutralize it.
In case of poisoning, it is necessary to put the patient to bed, you can give him a heating pad and strong tea. The stomach should be cleaned by drinking water with soda. After this, you must urgently call a doctor.
Share the publication - please colleagues
About mushroomsStudy Plan:
1. What is the kingdom of mushrooms (systematics) and what is its uniqueness.
2. Features of the structure
3. Power Features
4. Features of reproduction
5. The origin of mushrooms and further development by eras.
The Kingdom of Mushrooms (Mycota)
Mushrooms are an extensive group of organisms, numbering about 100 thousand species. It is worth highlighting several main classes of mushrooms.
Chytridiomycetes (@ 500 species)
Unicellular form of microscopic organisms
well developed intercellular mycelium
sexual process as zygotes (two cells merge, apparently not differentiated into male and female)
saprophytic fungus, develops well on wet bread
Ascomycetes (marsupials) @ 30 thousand species
special organs of reproduction (basidia)
some edible, some poisonous, some cause diseases of agricultural crops.
Imperfect mushrooms (deuteromycetes) @ 30 thousand species
multicellular mycelium
asexual reproduction
in the development cycle there are no sexual (perfect) forms of sporulation
some species produce antibiotics, formations on food, in the soil.
The uniqueness of mushrooms lies in the fact that they are very different from both animals and plants. Therefore, these organisms are isolated in a separate kingdom. We name some features characteristic of mushrooms:
glycogen reserve substance;
the presence of chitin (the island of which the outer skeleton of arthropods consists) in the cell walls
heterotrophic (i.e. nutrition by prepared org.
unlimited growth
absorption of food by absorption
spore multiplication
the presence of a cell wall
lack of ability to actively move
Mushrooms in structure and physiological functions are diverse and widespread in various habitats. Their sizes range from microscopic small (unicellular forms, for example, yeast) to large specimens, the fruit body of which in diameter reaches half a meter or more.
Features of the structure of mushrooms
The vegetative body of the fungus is represented by mycelium (or mycelium) -
A system of thin branching filaments (hyphae) characterized by apical growth and pronounced lateral branching. Part of the mycelium is located in the soil, is called soil (or substrate mycelium), the other part is external or air. Reproduction organs are formed on the aerial mycelium. In fungi, conventionally called inferior, the mycelium does not have partitions between cells, so the body of such an organism consists of one huge multinucleated cell. For example, mucor, which develops on vegetables, berries, fruits in the form of a white gun, and late blight, which causes rot of potato tubers.
In higher fungi, the mycelium is divided by partitions into separate cells containing one or more nuclei. In most mushrooms with an edible fruit body (with the exception of truffles, lines and morels), the fruit body is formed by a hemp and a hat. They consist of mycelium filaments closely adjacent to each other. In the hemp, all the threads are the same, and in the hat they form two layers — the upper one, covered with a skin dyed with different pigments and the lower one. In some mushrooms, the lower layer is penetrated by numerous tubules (porcini mushroom, boletus, grease nipples), these are tubular mushrooms, while in others, by platelets (mushrooms, russula are lamellar mushrooms).
Mushroom cells are covered with a hard shell-cell wall, which consists of polysaccharides 80-90% (in most it is chitin). There can be one or several cores. Of the organelles of the fungal cell, mitochondria, lysosomes, vacuoles containing nutrient reserves in-in should be called. The role of the reserve is performed by glycogen. Mushrooms do not have starch. Cells do not contain plastids and chlorophyll; therefore, fungi cannot photosynthesize.
Power Features
The digestion of fungi is external - they secrete hydrolytic enzymes that break down complex organic substances, and absorb the hydrolysis products throughout the surface of the body.
Saprophyte fungi feed on dead organic matter. They play an important role in the cycle of substances in nature, mineralizing organic substances, freeing the soil from dead residues and at the same time replenishing in it the reserves of mineral salts, which serve as food for green plants.
Symbiotic mushrooms are involved in the creation of two very important types of symbiotic union: lichens and mycorrhiza. Lichens are a symbiotic association of fungus and algae. Lichens, as a rule, settle on exposed rocks, in gloomy forests; they also hang from trees. A characteristic feature of fungi is their ability to enter into symbiotic relationships with other organisms. In fungi, such a symbiosis is called mycorrhiza (or In fungus root) - the association of the fungus with the root of the plant. Such an alliance is very beneficial to both partners. As a result, the fungus receives a large amount of organic substances and vitamins, and the plant component becomes able to more efficiently absorb nutrients from the soil (partly due to the increase in the absorption surface, and partly because the fungus hydrolyzes some of the compounds inaccessible to the plant). The number of plants capable of forming mycorrhiza is very large, for example, it does not occur in flowering plants only in the family of cruciferous and sedge. Depending on whether fungal hyphae penetrate into root cells or not, they distinguish between endo- and ectomycorrhiza.
Propagation Features
Mushrooms have vegetative, asexual and sexual reproduction:
Vegetative propagation is carried out by parts of the mycelium, which, being separated from the total mass, are able to grow and develop independently. In yeast fungi, vegetative propagation occurs by budding: outgrowths (buds) form on the mycelial cells, gradually increase in size, and then become laced.
Asexual reproduction is carried out by spores. What kind of disputes are there, with and without flagella, single and covered with a common shell. The container of the spore is called sporangia, and the hypha on which it is located is the sporangien. Zoospores (spores with flagella) are in zoosporangia. If the spores do not have flagella, then they are called conidia and openly sit on a coniferous bearer. Spores can develop either inside the sporangia (endogenously), or detach from the ends of special outgrowths of the mycelium (exogenously).
The simplest arranged lower fungi most often live in water. The spores of these fungi have flagella and swim beautifully. This is the first way to dispute spores.
Mold spores are very small and light, so they can easily spread through the air, through water, on the legs of insects. Drops of rain can carry large mushroom spores. Animals also participate in the spread of many spores. Especially often they are used by mushrooms, the fruiting bodies of which are located underground, for example, truffles. Spores of fungi and insects spread. Then mushrooms often have a specific smell and mucous secretions.
Another way is spreading spores with elastic hyphae (peronospores) or a shooting sporangia (pilobolus)
Methods of resettlement of mushrooms are divided into passive and active. When passive, the fungus uses someone else’s help, and when actively, M copes with it. Note that the greater the choice of carriers, the easier the resettlement devices of the fungus. In addition, the less spores a mushroom forms, the better they are protected and adapted.
Spores germinate in the growth tube from which the mycelium develops.
Reproductive opportunities are enormous - a single fruiting body can bring 1 billion spores per year.
3) But the dispute gives only the beginning of the primary mycelium. Two spores sprouted nearby and the primary mycelia merged, giving rise to the secondary mycelium (this is the sexual process) E The sexual process consists in the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of a zygote. In lower fungi, gametes are motile; they can be the same in size (isogamy) or different (heterogamy). If gametes differ not only in size but also in structure, they are formed in female (oogony) and male
(anteridia) genitals. A fixed egg is fertilized either by motile spermatozoa, or by an outgrowth of anteridia, which transfuses its contents into oogonia. In some fungi, the sexual process consists in conjugation of two identical at the ends of the mycelium. The secondary mycelium grows, feeds, and in favorable conditions forms new fruiting bodies. Why does the fungus have fruiting bodies? A new generation of mushrooms is being prepared in their established UkuhnneF: spores protected from unfavorable conditions are laid and mature. And, having matured, spores with the help of fruiting bodies fly away from the parent mushroom.
Any living organism, and a mushroom is no exception, inherits a program for further development, and if conditions allow, it implements it. Hereditary information is contained in the nuclei of cells. Mycelia come with a full program (diploid)
Or only with its half (haploid). In the first case, they develop normally, and in the second, in order not to dwell on the development of the Middle Path, merging with the other haploid half with the combination of hereditary information and the formation of a new diploid organism is required.
Mushrooms have two developmental options after this merger:
The first is observed if the diploid stage is short-lived. Then, after the sexual process, reduction fission quickly occurs (i.e., the nuclei fuse and divide twice), which leads to the formation of haploid structures. The fungus immediately proceeds to the formation of spores, having supplied each of the halves of the half hereditary program.
In some fungi, at the end of the reproductive process, a cell forms with two nuclei that come from both parents and a reduction division occurs. The result is a bag with eight haploid spores. Such mushrooms are called marsupials.
Other fungi also form a cell with two nuclei, which merge and divide twice. But the haploid spores are not in the bag, but on special outgrowths of the swollen basidium cell.
Well, the second option is found in fungi, In hibernating F after cell fusion. Their diploid cell (zygote) is covered with a thick membrane and will wait for spring. And after waiting for F, it grows: reduction division occurs and haploid spores are already developing.
Considering the peculiarities of the structure, nutrition, and reproduction of mushrooms, we can say that these amazing organisms are perfectly adapted to environmental conditions. How did they achieve all this? For this, it is necessary to trace the development of mushrooms over a huge period of time.
The origin of mushrooms and further development by eras.
Eukaryotes
Most researchers admit that shortly after the emergence of life on earth, it was divided into three roots, which can be called suprasternies.
The eukaryotic overworld very early, apparently more than a billion years ago, divided into the kingdoms of animals, plants and mushrooms. Mushrooms are closer to animals than to plants. Finally, a small group of slimes is so peculiar that it can only with difficulty be included in the kingdom of mushrooms, with which it is traditionally combined. Apparently, multicellularity arose independently in fungi, plants, etc.
Mushrooms are ancient organisms. Their minerals are about 900 million years old. It is possible that they are one of the first eukaryotes.
It is widely believed that fungi originated from the algae with which they are most similar. However, a number of botanists believe that algae and fungi had only common ancestors from the flagellum group. There is no consensus on the question whether fungi are monophilic, that is, they have one common ancestor or are polyphilic, that is, they came from different groups.
Be that as it may, but by the end of the Ameno-Carboniferous period (about 300 million years), they had already reached considerable diversity.
Here we directly come up with the question: How did these plants belonging to the group of lower plants not only adapt, but also flourish successfully?
To do this, let's see how mushrooms developed.
Mushrooms are eukaryotes. When eukaryotes arose, science is not known. Studies at the molecular level have led some scientists to suggest that eukaryotes can be as ancient as prokaryotes. In the geological record, signs of eukaryotic activity appeared approximately 1.8–2 billion years ago. The first eukaryotes were unicellular organisms. Apparently, they have already formed such fundamental signs of eukaryotes as mitosis, membrane organelles.
As the aquatic environment dominated in Archean and Proterozoic, our planet underwent significant shocks: there was very high geothermal activity, active mountain building was going on, glaciation was replaced by climate warming. In the atmosphere, the oxygen content increased to 5-6% of the current level, all this created favorable conditions for the existence of not only multicellular animals and plants, but also fungi. These changes in the habitat have also affected the formation of a large number of new species of animals, plants, and fungi.
About 1.5 billion years ago, one of the most important aromorphoses, sexual reproduction, arose.
The environmental conditions of the next Paleozoic era also contributed to the rapid development of eukaryotes, and hence fungi. As for the climate during this period, it was quite moderate, humidity increased. And the land split into separate continents, which were grouped near the equator. This led to the creation of a large number of coastal areas suitable for the resettlement of living organisms.
This period of time gives us very little information about mushrooms, since their fossil record is almost unknown.
Silurian period of the Proterozoic era is characterized by the emergence of plants on land, caused by an increase in land area. Such plants are called psilophytes. In my opinion, mushrooms could also go on land following plants. It is even possible that they have such aromorphosis as mycorrhiza with these plants, because they needed substances that they themselves could not synthesize.
In the Devonian period, the rise of land continues. The climate is characterized by a change in dry and rainy seasons. Icing in modern South Africa and America. Due to the instability of the climate, the mushrooms needed to improve their organs and tissues, as well as the reproductive system, in order to protect themselves from extinction. So, for example, in the event of a cooling, the zygote could hibernate before warming and become covered with a hard shell that protects the seeds from cold and adverse conditions.
In Carbon (the Carboniferous period), the worldwide spread of forest swamps began. Evenly warm and humid climate is replaced at the end of the period by cold and dry. The period ends with extensive glaciation of the southern continents. Before the unification in the swamps, aquatic forms of amoeba-like mushrooms could appear and, as has already been noted, mushrooms have already reached a considerable variety
In the Perm period, despite the cooling of the climate and its dryness, gymnosperms and mushrooms became widespread.
Forced to live on land mushrooms, had to adapt to the prevailing conditions. But the climate is not too warm. And the bodies of the mushrooms began to be covered with a hard shell, due to chitin in the cell walls, but the amoeba-like mushrooms were preserved.
The Cenozoic era marked the establishment of a warm and even climate. The dominance of angiosperms, a significant number of groups that emerged in the Cretaceous period. The composition is close to modern. Prosperity of plants, animals, insects and fungi.
Conclusion by eras:
Amazing mushroom organisms. Throughout their development, they fought for survival only with natural conditions, and plants and animals not only did not interfere, but also actively helped themselves and them. The animals themselves, without noticing it, helped spread the spores of the mushrooms, thereby preventing them from dying, and the plants U with pleasure entered into mycorrhiza with mushrooms. Fungi responded to all aromatic changes with the necessary aromorphoses.
Conclusion throughout the work:
Mushrooms, one of the first eukaryotes, not only survived, but also successfully thrive due to the fact that:
Mushrooms have acquired such an important aromorphosis as mycorrhiza. They depend on plants, but plants depend on them. This is extremely beneficial for mushrooms cohabitation, which has developed over many millions of years.
The variety of mushrooms is so great that they occupy both the aquatic and airborne habitats. Their structure is also diverse. This gives them an advantage and increases the chance of survival of the entire kingdom as a whole.
Three ways of reproduction. Even if the mushrooms find themselves in conditions where one of the methods cannot be applied, due to adverse conditions or, for example, lack of water, it will be possible to use the other two. Again, the survival rate is higher.
Bibliography:
I.Yu. Pavlov U Biology. Tutorial Manual
Biology textbook Maleeva Yu.V.
Ed. House UDrofaF UBiologiya- FloraF
V.A. Korchagi U Biology 6-7 classF
Materials from the site www.defacto.ru
A.V. Yablokov, F. Yusufov UE
B. B. Zakharov U Biology - general laws
Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine
Donetsk State University of Economics and Trade
them. M. Tugan-Baronovsky
Department of Production Technology
catering products
abstract
on the topic :” Mushrooms and their use ”
Supervisor : associate Professor V. Davydova
Performed : student of group TN-02a
Dovbenko M.V.
Donetsk-2002
1. General characteristics of mushrooms
2.Dividing mushrooms by lifestyle.
3. Edible mushrooms.
4. Small edible mushrooms.
5. Inedible mushrooms.
6. Nutritional value.
7. The rules for collecting mushrooms.
8. Mechanical processing of mushrooms.
9. Preservation of mushrooms
a) pickling
b) fermentation
c) salting
d) mushrooms in their own juice
e) fried
e) mushroom extract
g) drying of mushrooms
h) mushroom powder
10. Assortment, cooking technology.
11. Characterization of medicinal mushrooms.
12. Characteristics of oyster mushrooms.
13. Prevention of mushroom poisoning.
1. Mushrooms are a very large group of plant organisms in nature. They are studied by a special science - mycology (from the Greek. "Mikos" - mushroom), it explores plants, systematics, ecology and biology of mushroom organisms.
Mushrooms are diverse in shape, size and functions that they perform in the environment. Science knows more than 100 thousand species of mushrooms. Among them, the most famous are cap mushrooms used in nutrition, yeast, used in the food industry (bakery, winemaking, brewing, etc.), mold fungi that cause diseases to plants, people, animals, and others. Many sectors of the economy deal with mushrooms. Mushrooms also play the role of orderlies on the planet, decomposing dead organic matter, and also participate in the processing of numerous waste products from human activities and industries.
Since ancient times, mushrooms have been used in nutrition. The number of mushrooms that are considered edible in different countries is not the same. So, in Slovakia up to 58 types of mushrooms are allowed for sale, in Ukraine only 16.
In Europe, there are about 500 species of edible mushrooms, but only 80-100 species are used in food. But you must always remember that the use of well-known and doubtful mushrooms must be careful, since the effect of mushrooms on the human body is often manifested individually
People knew about mushrooms a very long time ago. The French botanist Voiley in 1718, performed in Paris, described the mushrooms as a diabolical work that violates the general harmony of nature. He stated that the mushrooms were created by the devil in order to listen to the most talented researchers and to drive the nerds in despair.
In the 4th century BC, the Greek scientist Tiofrast mentioned truffles, morels, champignons in his writings. After 5 centuries, the Roman naturalist Pliny also wrote about mushrooms. He was the first to try to divide the mushrooms into useful and harmful. The ancient Romans knew well what poisonous mushrooms could do. When it happened, it was necessary to remove a statesman, in ancient Rome they served him a dish richly seasoned with poisonous mushrooms.
The most incredible fabrications and fables were written about mushrooms. Their sudden abundant appearance was explained as a result of a lightning strike. A good harvest of mushrooms was considered in some places a bad omen, in others - a good one. People have noticed that some of the mushrooms grow, forming a regular circle, the grass inside of which dries up. Having no answer to the riddle, they associated this phenomenon with evil spirits. In Holland, these circles were considered the place of storage of enchanted treasures, in Germany - the place of witches dancing.
The origin and life of mushrooms was a mystery to humans. For a very long time, some scientists thought that mushrooms are not plants, but animals
opportunism. The famous Swedish scientist-naturalist Karl Liney, who believed that mushrooms are similar to polyps, was of the same opinion. Only later did he change his point of view and take mushrooms to terrestrial plants.
In fact, these are amazing plants. They have no roots or leaves, they do not bloom and do not produce ordinary fruits with seeds. The botanists of the past knew that they reproduce not by seeds, but by spores.
At present, it is already known that fungi belong to lower plant organisms in the cells of which there are no chlorophyll grains, therefore they are deprived of the opportunity to assimilate carbon from carbon dioxide in the air, and they feed and use organic substances of the environment on which they develop. Mushrooms, as it were, are the fruits that we pluck from the mycelium tree. It is located underground. The old perennial mycelium is a large ring on which mushrooms grow. The mycelium consists of interwoven threads. It resembles a loose layer of felt. From it, the fruiting body develops. The mycelium supplies the fruiting bodies with nutrients, but under adverse conditions it does not develop, but passes into a state of suspended animation.
Edible mushrooms are combined in a group of hat mushrooms, because they consist of hats, legs and hemp. Edible mushrooms also include mushrooms, which differ in structure from hat mushrooms - these are lines, morels and truffles.
Bionts are mushrooms that coexist with the roots of higher plants by combining the roots of trees with mycelium.
Mushrooms occupy not a small proportion in human nutrition. Mushroom picking grows annually and reaches a huge amount. Meanwhile, mushrooms are consumed not only by humans, but also by the animal kingdom, and also in large quantities. So, for example, a herd of deer after prolonged protein starvation rises in the upland tundra, where after summer rains a large number of mushrooms and feed exclusively on them until snow falls. Mushrooms and squirrels are stocked for the winter. About 116 mushrooms were found in the nest of one such mistress, and more than 1,500 were found in the other.
For the favorable development of mushrooms, a certain temperature and humidity is required. If the autumn was warm and rainy, then next year there will be a good harvest. On average, abundant harvests of mushrooms occur once every 4 years. But there has not yet been such a year that the crop failure of mushrooms is repeated throughout the country. If there are no mushrooms in one part of the country, then they will be in another.
The assortment of mushrooms is very large. There are about 200 species of cap mushrooms, but a person eats about 40 species, and in some places 15-20 species. All other fungi are either poisonous or little known. But all the mushrooms, which are edible, have found very wide application.
The fruit body consists of a hat and legs supporting it. The hats have a different shape, they consist of pulp coated on top with a protective skin of various colors and a lower spore-bearing layer, which can be tubular or lamellar. The plates are attached differently to the leg: they do not reach the leg or are widely attached to it. Differently arranged plates to each other. The shape and arrangement of the plates depends on the stage of development of the fruiting body of the fungus.
Some lamellar mushrooms, less often tubular ones, are covered with a special veil that breaks as it grows, forming a collar, flakes, scales or warts on the cap on the stem.
To recognize an edible fungus, one needs to know its shape and color, which can change with age or with weather, soil, season. The peel is smooth, scaly, warty, mucous, densely and loosely fused with flesh.
The pulp of mushrooms is varied in color, can change color during storage. In some fungi at the break, milky juice of various colors is released. Some mushrooms have a specific smell.
The legs of the mushrooms are located centrally, eccentrically, from the side. From the outside, they can be smooth or finely fibrous, sometimes with a grid pattern. In some mushrooms, the legs are covered with scales of various colors, either with or without a cuff-like ring. Mostly the legs are round or cylindrical in shape. According to the internal structure - filled with flesh or hollow, and some inside are lined with loose lattice flesh.
3. White mushroom (boletus) - the most valuable mushroom. He is called the "king of mushrooms." However, in Switzerland it is considered inedible. He belongs to the group tubular mushrooms. It grows mainly in pine forests, in spruce and mixed forests. The hat is dry, smooth, brown or light brown. Leg in the lower part is expanded, light brownish, and in the upper part with a white mesh pattern. The pulp is white, dense, with a sweet taste, with a pleasant smell of slightly toasted walnut. This is a mushroom that reaches a wide variety of sizes. So, for example, near Vladimir they found a mushroom about 40 cm high, 60 cm wide hat, 26 cm thick legs and 6 kg weigh, without a single wormhole. A fairly large specimen of the fungus was found in Leningrad region. He had a hat with a diameter of 21x27 cm, 9 cm thick, a leg length of 14 cm and a width of 9 cm. The mushroom weighed 1.5 kg. White mushroom is widely used in nutrition. Porcini mushroom broth is 7 times more caloric than meat. Most often, dried mushroom is used, since it acquires a mushroom flavor. Ceps do not salt, but sometimes pickle.
An unusual exhibit appeared in the exhibition hall of the Vinnitsa regional branch of the Republican Society for the Protection of Nature. This is a mushroom, whose height is 25 cm, diameter - 35 cm, and weight over 2.5 kg.
Oil mushrooms are the most common mushrooms. The habitat of butterflies is the forest edges of mostly pine young forests. Therefore, they are also called "pine trees". Macs usually grow in rows and appear among the first. This is a very useful mushroom, although it contains little fat, only 0.3% (N. Volpr, 1975).
They have the following appearance: a large-pointed hat, covered with a dark brown or reddish oily skin. The underside of the fungus is covered with a white film, a dark pulp under the film. In writing, they are used in boiled, fried, pickled and salted form. In dried form are not used, because darken when drying.
Redheads are autumn mushrooms, but appear in large numbers in the summer months. They grow in pine forests. There are also spruce mushrooms (green) and pine forests (bright orange).
The spruce hat is thinner than that of the pine forest. The hat is fleshy, smooth. Leg color of the hat or a little lighter. With a break, juice of a bright orange color is pleasant to taste and smell. These mushrooms can be salted, fried and pickled.
Boletus is a white stump that wears a bright red velvet hat. Leg is dense, dark fibrous, scaly. It is used for cooking, frying, pickling and drying, has high taste properties.
Pereberezik - grows mainly in birch groves. It has three varieties: common boletus, pinkish and swamp. They differ from each other in growth time. Common boletus has been growing since July and throughout September. Swamp - only in September. This is the worst mushroom; its flesh is weak and watery. Pinking grows from August to September. The appearance of all three mushrooms is the same. The hat is gray, smooth, dry. Leg to the bottom thickened, solid, whitish. The pulp is white. It is used in dried and pickled form. Young boletuses are good to cook.
Volnushka - called so because on the hat on a bright pink field diverge more pale circles. It grows in a birch forest and appears in the summer already in the month of June. With a break, white milky juice is released, which is very bitter. Therefore, when cooking, they are soaked in cold water. There is a variety of trevushki - trevushka white. Its surface is a dirty color. It grows in birch and mixed forests, most often in young ones. It is mainly used for pickling and pickling.
Russula - grow in any forest. They can be eaten raw, because they are completely harmless. The hat is convex or funnel-shaped, of various shades, smooth with thin edges. In total there are 27 varieties of russula, 8 of them have caustic juice. Before use, they should be soaked in cold water. Other varieties can be consumed immediately.
Varieties of russula - brilliant, swamp, boron, yellow, greenish, fragile red, fragile purple and others. Real russules grow in August-September. They are used in boiled, fried, pickled and salted form.
Chanterelles - grow in deciduous and mixed forests. Appear in early June. These are very valuable mushrooms. They contain the largest amount of fat among mushrooms - 2.4%. The features of this mushroom are that the mushroom cap is convex with a curled edge, fleshy, smooth, yellow. The leg is short, extended upwards and the colors of the hat. The young mushroom contains vitamin B2. These mushrooms can be boiled, fried, pickled and salted.
Honey mushrooms are the most versatile mushroom. It can often be found on stumps in the felling areas. He is the only mushroom that is good in all forms. But it is harmful in relation to the forest. The honey agaric can affect about 200 plants: pines, spruce, oaks, fir, etc. He can live off dead wood. The honey agaric spreads not only by disputes, but also by rezoforms, which have the appearance of cords of dark brown color, 2-mm thick and several meters long. Resoforms are able to penetrate the roots of trees. Under the bark they form a mycelium. The cap is flat-round, chestnut-colored. The leg is hollow, thin. In young mushrooms, the hat is connected to the stem with a film; in adults, a ring remains from it.
Meadow honey mushrooms are found, they grow only in meadows. They have a strong and pleasant smell. Meadow mushroom also called clove fungus, because its smell is slightly clove. It can be fried, marinated and dried.
The real breast has a hat, convex-rounded with a funnel-shaped age, white, with sharply curled edges. The cap-colored leg is hollow inside. The pulp is sharp in taste, with a pleasant smell. Milky juice is white, in the air it turns gray-yellow. It tastes very pungent. Breast is used only for salting.
Polish mushroom - grows in the glades of mixed forests, the hat is dark brown, dry, slippery in wet weather. Leg color hat, smooth. The flesh in the air darkens slightly. It is used for boiling, frying, pickling and pickling. Dried mushroom has no aroma.
Kozlyak - the hat is dirty pinkish-brown, smooth, mucous in wet weather. The skin is mucous. The leg is often bent, dense, the color of the hat. The pulp is dense, yellowish-reddish-brown. This mushroom is a good antibiotic. In addition, it is a valuable product and is used for roasting, boiling, pickling and drying.
Green flywheel - very similar to polish mushroom, hat grayish or tan, dry. Leg is yellow or red, flesh is white, bluish on fracture. This mushroom is used only in fresh form - boiled or fried.
Pig - has a funnel-shaped hat, brownish-brown, leg, short, lighter. Used for frying.
Valui - a young mushroom has a spherical hat, and an adult has a flat, slimy, soft, yellow-brown color. The leg is white, dense. With a break, a watery, colorless, milky juice is secreted. Used only for pickling or pickling.
Belyanka - hat is convex, velvety, white in color with yellowish-red spots. The leg is dense, short, of the same color. With a break, white milky juice is secreted. It is used only for salting.
Black truffle - differs from other mushrooms in that it grows underground at a distance of 10-20cm from the surface. They look like potato tubers 2.5-3.5 cm in size. The surface is brownish black with warts, grayish inside. Truffles have long been considered very valuable mushrooms.
Pushkin in "Eugene Onegin" calls them "the luxury of a young age."
Truffles have a very pleasant and strong aroma, which allows them to be collected using specially trained dogs. The shape of the truffles and their growth brought to life the word "potato". And the French playwright Moliere gave the hero of one of his comedies the name Tartuffe, which in Russian means morel.
Garlic - a small mushroom with a thin leg. Flat hat
convex yellow-brown, thin as paper. The plates are white, frequent, narrow. Leg is dark brown, up to 5 cm long. The smell of the mushroom is garlic, where the name came from. These mushrooms can be fried, but it is best used for making sauces.
Morels are the earliest spring mushrooms. Appear immediately after the snow begins to melt. The cap of the mushroom is ovoid, with an uneven surface, dark or light brown, hollow inside. The hat gradually turns into a leg. Leg is smooth or slightly folded, inside is hollow, white, brittle. The pulp is white with a pleasant smell. Fresh morels contain 3% nitrogenous substances, 1% sugar and many aromatic substances.
A variety of morels is a morel cap. Unlike conic morels, a bell-shaped hat with a free edge that has not grown to the pedicle, wrinkled, brown, brownish, occasionally yellow. The leg is high, cylindrical, white or cream, hollow inside. The pulp is waxy. It is used boiled and fried. It grows in groups in aspen and linden forests.
The line is irregular in shape. Hat in deep folds, brown. Leg is cylindrical, yellowish in deep folds. The lines as well as morels contain 3% nitrogenous substances, 1% sugar and many aromatic substances. The edges of the cap partially fused with the leg. The pulp is thin waxy with a pronounced mushroom smell.
Champignons - agaric mushrooms. The cap is hemispherical, bony, white, yellowish or light brown. The leg is dense cylindrical. Vitamins A, gr. Found in champignons B, C and D, as well as enzymes of protoase, cytase, amylase, invertase, lipase, etc. The composition of nutrients depends on the soil on which the fungi grow. Champignons can be grown artificially.
The main ones are brown and white. Champignon bicuspid white has a white hat. This type of fungus is less productive and more susceptible to disease.
Champignon double-cured brown has a brown hat in different shades. Differs in high productivity and resistance to diseases.
The main thing in mushroom cultivation is the proper cultivation of mycelium. The mushroom picker is first grown on manure, and then used as a planting material.
Spider web mycelium turns into heavy, then into string and the fruits appear. For the normal cultivation of mushrooms, certain conditions must be observed. An important condition is humidity. At a moisture content of 40-50%, the spider mycelium grows mainly, at 50-60% it turns into a heavy mycelium, at 70% a cord mycelium appears.
Mycelium growth also varies depending on the composition and temperature of the nutrient medium. Excess carbon dioxide, poor oxygen availability, lack of water and nutrients inhibits the growth of mycelium. For greenhouses, they usually choose a site protected from cold winds, with dry soil and deep standing groundwater. Temperature, like humidity, requires different at different periods of growth. The higher the temperature of the nutrient substrate, the lower the room temperature should be. Light also has a negative effect on fungal growth.
The mushroom picker is planted at soil temperature up to 20-25C. It is divided into small groups of 30-40 g and planted in a checkerboard pattern, at a distance of 20-25cm from each other. Gather mushrooms, carefully twisting, and not tearing, so as not to tear out with it the mycelium.
Morels and stitches can also be grown relatively successfully. To do this, pieces of fruiting bodies, or lumps of forest soil with mycelium, are sown on a bed. After this, the beds are covered with humus and leaves. Wood ash is added to the soil. More difficult now is the culture of such cap mushrooms as porcini, camelina, breast. Some experiments have not yet yielded results, but much has already been done. Polish scientists managed to achieve the fruiting of the cep in the laboratory. Now there is no doubt that the culture of wild mushrooms is practically possible and in the future may become one of the sectors of the national economy.
4. In addition to the above-mentioned edible mushrooms, in the forests there are many more mushrooms that are unfamiliar or little known to consumers. Ego: oyster mushroom (ordinary, autumnal, carob-shaped), chrysanthemum, annular cap, pink onion, flake (golden, herbaceous), ordinary liverwort, horned, golovach, fluff, lobate, etc.
5. In the forest, among the edible mushrooms, you can often find poisonous mushrooms, which in appearance are similar to edible, but are dangerous and cause severe poisoning.
Pale toadstool is the most dangerous mushroom. AT middle lane it is rare, and in the southern zone, in particular in Ukraine, it is often plentiful. This mushroom grows in mixed birch forests and in oak. The cap of a pale toadstool is round-bell-shaped, white or light green. Hat plates are white, wide. Leg at the top is flat, and at the base thickened. Its flesh is white, slightly sweet in taste. In appearance, it is very similar to champignon, but differs in the presence of white plates, while in champignons they are light brown.
The bile fungus is similar to ceps and grows with it in the same period. The cap is hemispherical, brownish or light brown. The pulp is white, it tastes very bitter. Bile mushroom is considered not edible due to its bitter taste and poisonous.
The southern chanterelle is very similar to the chanterelle. This mushroom grows next to the real fox in pine forests. It differs in that the hat is round-funnel-shaped with round edges, while the edges of a real chanterelle are wrapped. The color of the hat is red-orange. The plates are bright red. The taste is unpleasant.
Amanita is the most common inedible mushroom. It has a specific color and cannot be confused with an edible mushroom. Amanita species are many and all are poisonous. Its varieties include: smelly fly agaric (by toxicity it is very close to a pale grebe), grebe-like, parfy. red panther, etc.
Satanic mushroom is most often found in the southern strip and in the Caucasus. III. The grayish or greenish foot. The pulp is white, sweet. With a break, it first turns red, and then turns blue. The leg of the mushroom is swollen with a red mesh pattern. This mushroom is similar to boletus and is very poisonous.
There is just inedible mushrooms due to unpleasant taste or smell. These are: pepper mushroom, false foam, false valuy, false raincoat (ordinary, warty). All these mushrooms cause poisoning of one degree or another.
6. Mushrooms - a valuable food product. 0 mushrooms S.T. Aksakov wrote: "Mushrooms make nutritious, tasty and healthy writing." They are the source of many minerals. No wonder, in the old days, during fasting, mushrooms were almost the main food of the population. Even on the king’s table, mushrooms occupied a prominent place. Life holds a lot of evidence that the nutritional value of mushrooms deserves attention. In Australia, one of the species of mushrooms was called "Australian bread."
Mushrooms are superior in nutrition to many vegetables and fruits, and in chemical composition and a number of characteristics, they approach products of animal origin. The broth of dried porcini mushrooms is superior in calorie meat. Therefore, the harvesting of mushrooms is of great importance in the national economy.
According to their nutritional value, mushrooms are divided into IV categories:
1 - porcini mushrooms, mushrooms, yellow mushrooms, mushrooms;
P - boletus, brown boletus, oily, aspen mushrooms, oak trees,
Winkles, polish mushroom;
Ш - mosses, goats, whites, ear-rings, valui, russula, chanterelles, honey mushrooms, champignons, lines, morels;
IV - violinists, rubella, bitter, pigs, greenfinchs, rank-and-file, oyster mushrooms.
This classification can be said to be conditional, because the quality of the finished product depends not only on the category, but also on how well the mushrooms are processed.
The nutritional value of mushrooms depends on various factors: meteorological conditions, soil, as well as the age of the mushrooms. Young mushrooms are more nutritious than overgrown, old ones.
Fresh mushrooms contain a significant amount of water, an average of 90%. During heat treatment, the amount of water is almost halved, while in the case of reduction it is reduced to a minimum. Dried mushrooms are often called plant meat, "because mushrooms contain a lot of protein and fiber. And yet, dried mushrooms are inferior to fresh ones in nutritional value, since the drying process reduces the content of nitrogenous substances, especially free amino acids.
As the data in table 1. show, mushrooms are closest to vegetables, but contain, in comparison with them, a large amount of protein.
Table 1.
The chemical composition of the mushrooms (in%).
Title | The energy. price. (kcal) |
||||||
Boletus | |||||||
Boletus | |||||||
Half of the dry residue in mushrooms is made up of nitrogenous substances, of which 58-75% are proteins. In relation to the fresh mass of mushrooms, proteins make up 2-5%. The composition of mushrooms in proteins varies depending on the type of mushrooms and parts of the fruiting body. Proteins are concentrated in mushroom caps, which are much more valuable than more dense, but less rich in nutrient legs. Studies of many years have shown that the proteins of some fungi (porcini, butterfish, boletus) are complete, i.e. contain all the essential amino acids. The rest - contain an incomplete set of essential amino acids. The main amino acids present are leucine, tyrosine, arginine, and glutamine. Their content ranges from 14-37% of the total amount of acids. They are good because they do not require the expenditure of digestive juices for their cleavage and are easily absorbed into the intestines. Ceps (8.6% of the dry residue) are especially rich in free amino acids. A lot of nitrogenous substances are non-protein (from 19 to 37% of total nitrogen). Fungin also belongs to nitrogenous substances, which gives strength to fungal cells, i.e. serves as the basis for supporting tissue (fungal fiber).
Fats in mushrooms contain from 0.1 to 0.9%. The composition of fats includes a very valuable substance - lycithin. Fat is found in fungi in the spore-bearing layer. The composition of fat includes glycerides of fatty acids and free fatty acids (palmitic, stearic, butyric, acetic).
The specific aroma of fresh mushrooms is known to change with various methods of processing mushrooms.
The main role in the formation of aroma of many plant products is played by volatile compounds. The composition of aromatic substances includes isovaleriandehyde, acetaldehyde, benzaldehyde, ethylbetyl ketone, methylcyclohexanone, etc. However, many volatile substances of the fungi are not identified, their composition is not determined.
By the number and composition of carbohydrates, mushrooms are close to vegetables, but there are carbohydrates that are not found in other foods. They include sugar, sugar alcohols, glycogen, fiber (0.2-1%). Sugar in mushrooms contains 2-16%, solids - 0.01-1.5% relative to the wet weight. Sugars are represented by glucose (0-4.2%), trigalose (0-1.67%).
Of sugar alcohols, mannitol is contained (0.2-0.7%), the oils also contain arabite. Mushrooms do not have starch, but there is glycogen identical to animal glycogen. Fiber of mushrooms is saturated with chitin. It not only is not digested, but also complicates the access of digestive juices to the rest of the mass. Tregazolite or lycotic (1.7%) improves the taste and increases the nutritional value of mushrooms. Mycoinulin and parodextrin are also present in the fungi, which cause the fungus to mucilage during prolonged
storage.
Table 2.
Minerals are half composed of potassium and one quarter of phosphorus. Calcium in mushrooms is almost as much as in fish. High phosphorus brings mushrooms closer to certain animal products. Mushrooms are valuable microelements (copper, iodine, zinc, arsenic), which are very visible during metabolism in the cells of human organism. Noticeably more of them in young mushrooms.
Rich in mushrooms and vitamins, especially groups B: B1, B2; PP There are more vitamins in mushrooms than in all other foods. Only yeast and liver are richer in them. Group B vitamins are especially rich in chanterelles. Ceps contain vitamin B1 (0.2-0.37%). In champignons, the amount of this vitamin is slightly less. Vitamin C contains 1-5 mcg%. The presence of vitamin B2, C and especially a lot of vitamin D was found in porcini mushrooms.
Vitamin A (0.9-6.7 mg%) is found only in some mushrooms (white, camelina, Polish), mainly in the form of carotene, which only after assimilation by the body turns into vitamin A.
Table 3.
The name of the mushrooms | ||
Boletus | ||
Boletus | ||
Russula |
Mushrooms are rich in enzymes - amylase, lipase, oxidoreductase, proteinase, etc. In older mushrooms, less valuable substances are found - purine compounds, urea, inorganic compounds.
Some fungi have bactericidal properties: in porcini mushrooms, the substance is hercenin, which reduces pain in angina pectoris, increases the vital activity of the human body; an oily substance was found in the oil that helps with headaches and gout; pepper breasts are used in the treatment of urolithiasis and as a diuretic; an antibiotic was found in the mountain cep mushroom, which stops the growth and development of many bacteria, as well as tuberculosis pathogens; raincoat and golovach are used in medicine as a hemostatic agent, an aqueous extract of the raincoat-giant inhibits the growth of malignant tumors; Amanita muscaria is poisonous, but is used for glandular tumors, tuberculosis and diseases of the nervous system. Folk remedy is water and alcohol tincture of fly agaric from rheumatism; pale grebe treated with cholera; mushrooms are used to treat frostbite parts of the body.
Many fungi accumulate antibiotics, others inhibit the development of pathogens of diphtheria, meningitis, tuberculosis, plague, etc.
An antibiotic lactovioriolin was obtained from camelina, which inhibits the growth of various harmful bacteria. From govorushki was obtained a new antimicrobial substance, which is used in the treatment of tuberculosis of the skin and bones. A deadly antibiotic for Koch's bacillus was found in a white fungus.
The honey agaric turned out to be active in the fight against E. coli, staphylococcus, etc.
There is no doubt that mushrooms have not yet revealed to people all their secrets. More recently, Japanese and American scientists have found that porcini mushroom contains antitumor substances. Czechoslovak scientists have found that gray dung beetle can be used to treat alcoholism. In India, a preparation of champignons was obtained, which is used in the treatment of typhoid sticks. In Japan, natural rubber was obtained from edible cap mushrooms, which has the same color and quality as rubber from rubber-bearing wood.
Mushrooms are also valued as a product. Mushrooms seasonings have been widely used for other dishes, as they give aroma and pleasant taste. The aromatic substances contained in the mushrooms increase appetite, secretion of gastric juice, contribute to a better metabolism, digestion and assimilation of food, and strengthening the nervous system. In the diet of children mushroom dishes it must be turned on carefully, and with a disease of the kidneys or gastrointestinal tract, mushrooms are contraindicated.
The hotness characteristic of some fungi is due to the presence of resins (terpene substances).
Of particular note is champignon mushroom. The name "champignons" is French, while all other mushrooms are Russian. This mushroom can be grown in champignon mushrooms all year round. Champignons take pride of place among mushrooms, they contain a lot of proteins, fats, mineral salts. Over 200 lats are already engaged in the artificial cultivation of champignons. For the first time, these mushrooms appeared in France in the 17th century, which is why they got the French name. Then they spread to England, Polyp, USA, Bangria and other countries.
In Russia, mushrooms began to be bred at the beginning of the XIX century. In St. Petersburg in 1861 there were only 10 champignons, and by 1900 there were already 100 of them.
A lot of research work has begun on the study of champignons. Currently, the culture of these mushrooms is mastered everywhere.
Opinion on the nutritional value of champignons is quite controversial. Champignons, like ceps, are rich in proteins (6.4%), fats (0.54%), carbohydrates (0.3%). From carbohydrates, champignons contain: sugar, trigolazagribny sugar, glucose. Of the polysaccharides found glycogen - animal starch, fungal fiber - fungin and hemicellulose. Fats and fatty acids in the dry matter of the fungus contain 2-5%.
The composition of fats includes a very valuable substance - lecithin. Also contains acids - oxalic, malic, tartaric. In old mushrooms, cholesterol and choline are often found - decomposition products of fat-like substances, as well as various alkaloids. These substances cause digestive and circulatory disorders. Therefore, mushrooms with unopened hats or opened, but not yet dark brown plates on the underside should be eaten.
Urea up to 13% was found in champignons, which in the presence of carbohydrates can be synthesized into amino acids.
The most poisonous and most terrible fungus is the pale toadstool. It contains the strongest poison - folloidin, which retains its toxicity even when boiled at 100 ° C. It does not dissolve in water, remaining in fungal tissues. The first signs of poisoning with this fungus appear 10-12 and even 30 hours after ingestion. Headache, dizziness, visual impairment, cramps in the limbs appear. There is a strong thirst and severe pain in the stomach, the temperature drops to 35 ° C. Then the attacks subside and after 2 hours are repeated again. With untimely assistance, 90 out of 100 people die. No processing methods reduce the toxic properties of mushrooms.
Amanita mushrooms cause mild poisoning, and in some cases, especially in children, can be fatal. The toxic effect of red fly agaric is caused by the presence of alkoloidamuscorin in its tissues. The initial poisoning with this fungus is expressed in severe intoxication. After 1-2 hours, vomiting, dizziness, stomach pain and cold sweat appear. If the poisoning is mild, then recovery occurs in 2-3 days
Conditionally edible mushrooms, stitches and morels, if they are not boiled or drained before frying, cause poisoning, which can be fatal. The tissues of these fungi have guillic acid, which causes severe poisoning.
In addition to poisoning, fungi can also bring about an upset stomach. Gastric disorders are caused by edible fungi, if they are not benign, i.e. overripe, worms, stored for more than a day, or salted and pickled mushrooms stored in aluminum or zinc dishes. Signs of poisoning are detected quickly and are accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Recovery comes in a few hours. Mild poisoning can be caused by improperly prepared threes, sows, chernushki, breasts, and valuys. For any poisoning, you must immediately call a doctor. Before his arrival, the patient should be put to bed, on the legs and stomach put heating pads and drink in small sips of salted water or strong tea, coffee.
But, despite the fact that some mushrooms are harmful, their bulk is a very valuable food product, which is not only possible, but also necessary for use in the human diet.
7. When picking mushrooms, it is necessary to trim the leg at the base. If the mushroom is not very familiar by external signs, then it is carefully pulled out and inspected the lower part, the signs are determined by which it can be attributed to a certain species and to edible mushrooms.
It is better to put mushrooms in low baskets so that they do not break. To clean the mushrooms using small stainless steel knives. You can not collect unfamiliar, overripe and wormy mushrooms. When cleaning mushrooms from debris, it is necessary to carefully check the species affiliation once again.
8. Sorting of mushrooms.
Each type of mushroom has its own taste and processing method. Some mushrooms can be fried fresh, while others only after boiling. But it’s best to pre-boil all the mushrooms, and then apply other types of heat treatment, although the taste in some of them decreases.
It is advisable to distribute the mushrooms in size, to facilitate their subsequent processing.
Cleaning mushrooms from debris.
Needles, moss, leaves and other forest debris are cleaned with a soft brush, cotton swab or soft cloth. From the top of the hat, the garbage is removed with a knife, because he sometimes sticks very tightly. From the folds of the mushroom, dirt is removed with a brush. For drying, the mushrooms should be especially thoroughly cleaned of contamination, and the damaged, darkened and softened parts are cut with a knife. In very mature mushrooms, the spore-bearing part of the cap is cut off. In some mushrooms, the leg has a viscous consistency, it is completely cut off. In russula, later butter, starting from the edges, peel off the hat, because after heat treatment, it becomes mucous.
Washing and soaking mushrooms.
You should not get involved in prolonged washing of mushrooms, as they absorb a very large amount of water and their consistency worsens. It is better to rinse them under running water and let the water drain. Porcini mushrooms are poured 2-3 times with boiling water, tubular and plate boiled for 4-5 minutes. This is necessary to reduce the volume, give softness, eliminate crumbling during slicing.
To remove the acid that is harmful to the body from the marsupial mushrooms, which passes into water during cooking, boil them twice in boiling water, after each boil, pour the broth and wash the mushrooms with hot water.
Dried mushrooms are washed several times in warm water and soaked in cold for 2-4 hours. After that, these mushrooms are boiled without salt in the water in which they swelled for 40-60 minutes. When using salted and pickled mushrooms, they are separated from the brine and spices are removed. Excess salt and vinegar are removed by washing or soaking.
In addition to cooking, mushrooms are subjected to: stewing, stewing, frying, baking.
Washed large mushrooms are cut into pieces. Porcini mushrooms, champignons, saffron mushrooms, russula are consumed along with the legs. In other mushrooms, the legs are separated from the hat, the hat is cut into identical pieces, and the leg is cut into circles.
Heat treatment of mushrooms.
Heat treatment significantly changes the properties of mushrooms. First of all, it reduces or eliminates their toxicity, eliminates the bitter taste, lowers the nutritional value and weakens their taste and aroma.
It is imperative to cook mushrooms that contain poisonous substances that dissolve in water: ordinary stitches, russula brittle, pink waves, pink and yellow breasts. They are boiled in large quantities of water for 15-20 minutes and the broth is drained.
Because of the bitter taste of heat treatment, they require bitter, real breasts, white ones, fireboxes, pigs and others. They are boiled for 5-15 minutes, so that the bitter taste disappears.
You can apply such methods of heat treatment:
Bring the water to a boil (1 liter of water 1/2 tablespoon of salt), lower the mushrooms and stand for 5-15 minutes, and then quickly rinse with cold water and allow to drain;
Mushrooms are dipped in cold salted water, brought to a boil, removed from the heat and allowed to cool in the same water.
It is impossible to dry mushrooms with the help of cargo, because they crumble and lose a lot of nutrients.
For some types of processing, mushrooms are blanched (russula, mushrooms). They are poured over with boiling water or immersed in boiling water for several minutes, or kept over steam.
If the mushrooms cannot be processed on the day of collection, then they can be stored one night in a purified form, but without rinsing or cutting them, in a cold room or in the refrigerator at t 2 ... 6 C.
If the mushrooms are cooked, then they can be poured with cold water.
During heat treatment in mushrooms, various physicochemical changes occur, as a result of which they acquire new properties characteristic of culinary-processed products. They acquire a pleasant taste and smell, which contributes to better absorption of products. The importance of heat treatment is that it destroys microorganisms located on the surface of the raw material.
When cooking mushrooms to some extent, softening of the tissue occurs. The main reason for this is the physicochemical changes in carbohydrate cell walls. The shell of fungal cells is fiber impregnated with chitin. This is the main carbohydrate in the cell walls.
The connection between cells during heat treatment becomes weak. The dissolution of pectin substances, half-cellulose cell membranes weakens them, but does not lead to complete destruction. Since there is fat in mushrooms, a partial change occurs during heat treatment. The hydrolysis of fats is accompanied by oxidation, since free fatty acids oxidize to knowledge faster than glycerides. Proteins during heat treatment denature, coagulate in protoplasm and cellular juice. When coagulation of protoplasm, the skin layer is destroyed and there is a diffusion of substances of cell juice through cell membranes.
This leads to the fact that when cooking, steaming and stewing reduces sya mass of mushrooms, as there is a loss of water and nutrients as a result of their diffusion into the broth.
Mushrooms mainly contain vitamins of groups A, B, C and D. It has been proved by many studies that vitamin A is preserved completely or almost completely during heat treatment. B vitamins are partially destroyed, part of them during cooking and stewing goes into a decoction. Of all the B vitamins, only B1 (riboflorin) can be distinguished, which is most resistant to heat, regardless of the method of processing its loss is not more than 11%.
The loss of vitamins also depends on the amount of water taken for a decoction. The more water, the less vitamins remain in the product. Vitamin PP is significantly better preserved than B1 and B2.
Those mushrooms that soften better, i.e. in which protopectin manages to convert to pectin during the formation of the crust.
For baking, mushrooms are pre-cooked. When baking, the same processes occur as when cooking. However, some processes are different.
This is the formation of melanoidins in the crust, caramelization of sugars. The formation of a specific taste and smell is due to the formation of new substances during heat treatment.
When cooking mushrooms, various volatile substances are released that are not found in foods in raw form. A constant component of volatile substances is hydrogen sulfide. It is formed as a result of post-denaturation changes in proteins. Hydrogen sulfide is formed, smoothly, as a result of the removal of sulfur, which is part of amino acids. These substances dissolve in the water in which the product is cooked. Thus, they play a significant role in shaping the taste and smell of boiled mushrooms.
The formation of a specific taste and smell during frying and baking is caused by melanoidins, as well as the breakdown products of proteins and carbohydrates.
9. Not only fresh mushrooms are valued and used in public catering, but also canned mushrooms. Mushrooms are harvested and processed from early spring to late autumn. The very first mushrooms appear in early April. These are lines and morels. In the first half of August there appear brown boletus, boletus, porcini mushroom, russula. Their most abundant growth at the end of summer is August and September. At this time, saffron mushrooms, greenfinch, honey agarics, and waves.
Canning is a very common way of harvesting mushrooms for the winter. Fresh mushrooms are perishable, so they are immediately pickled, salted and canned, and then used in cooking. Basically, all conservation methods are based on the principle of biosis - the complete cessation of the activity of microorganisms. The method of preservation is based on the action of high temperatures, antiseptics, antibiotics.
Pasteurization and sterilization are based on the action of high temperatures. Pasteurization is carried out at a temperature of 63 ... 92 C. During the pasteurization process, all forms of microorganisms and their spores are almost completely or completely destroyed. For these purposes, sterilization with a temperature regime of 105 ... 120 C. is also used.
Preservation with antiseptics is based on their interaction with the proteins of microbial cells, as a result of which the vital functions of microbes are paralyzed. Such substances are onions, horseradish, garlic and other products used in canning.
Antibiotics are substances of biological origin. They are products that have a destructive effect on microorganisms. Antibiotics are widely used in canning. Streptomycin, chlormycetin, biomycin, etc. are used as them. The use of various preservation methods is associated with changes that damage the quality of the products. It is necessary to apply such
canning method, in which longer storage and maximum preservation of product quality are possible.
In the production of mushroom products, the main operations are: washing, blanching and sterilization. When canning, some changes in nutritional and biological value occur in mushrooms. So, when canning mushrooms, chanterelles, butter, the following changes in B vitamins were revealed by the stages of their processing:
a) washing does not bring significant changes to the content of vitamin B in mushrooms
b) sterilization causes a decrease in vitamin B and the nature of the changes depends on the application of the thermal regime;
c) upon blanching, the content of riboflavin decreases to 85% in chanterelles, to 60% in honey agarics. But at the same time, nicotinic acid turned out to be very stable. Even with blanching, it persisted to Zb, 4%.
Sterilization time 2 minutes. It is the optimal shelf life of the vitamin B. Loss of nicotinic acid during sterilization is practically absent and only at a temperature of 120 ° C they make up 14-30%.
For canning, they mainly use porcini mushrooms, boletus. boletus, butter, chanterelles, champignons. The raw materials are carefully checked, selecting dense, undamaged, fresh, whole mushrooms, cut the legs and rinse well. Then blanch in a boiling 2% salt solution for 4-5 minutes, cool, put in glass jars, fill with brine, hermetically sealed and sterilized. After sterilization, the cans are cooled. Store in a dry, clean room at a temperature of 0-15 C.
1. Marinating mushrooms.
For pickling use porcini mushrooms, boletus. honey mushrooms, mushrooms, oily, boletus, chanterelles. mushrooms.
Mushrooms at the beginning prepare for pickling. To do this, they are cleaned of contamination, sorted by type and size, cut roots and put the mushrooms for 30-40 minutes to soak. After that, they are washed well and boiled in a stainless steel boiler. Salt is put in the boiler, poured with water and boiled for 8-10 minutes. Before the end of cooking add acetic acid, spices. After cooling, the mushrooms are packaged in glassware or barrels and corked. Instead of acetic acid, you can use citric acid, but its effect during storage of mushrooms is much weaker. Of the spices for pickling, based on 1 kg of mushrooms, up to 10-15 peas of bitter pepper, 8-10 peas of allspice, 2 bay leaves, 1-2 onions, 1 carrot are used. When pickling porcini mushrooms add a little nutmeg, sugar, for bitter - cloves (5-6pcs).
You can marinate mushrooms with tomatoes, cucumbers, cauliflower, bean pods. Prepared vegetables and mushrooms are laid in layers in jars, pour marinade with spices, sterilized for 60 minutes. The composition of this salad may vary depending on the season
2. Salting of mushrooms.
The method of pickling mushrooms is based on the conversion of sugar contained in mushrooms under the action of lactic acid bacteria into lactic acid.
Lactic acid, accumulating, prevents the development of putrefactive bacteria and thereby protects the fungi from spoilage.
Lactic acid is a conservative for mushrooms.
For the successful salting of mushrooms, it is necessary to provide favorable conditions for the life of lactic acid bacteria.
These are the following conditions:
Adequate sugar content. The less sugar there is, the less lactic acid will be obtained, and therefore, the less stable the products will be during storage;
The most favorable temperatures for the life of lactic acid bacteria. These temperatures are: from 15 to 22 ° C. If the temperature is below 15 ° C, then lactic acid bacteria will develop slowly. At temperatures above 22 ° C, in addition to lactic acid bacteria, other harmful microbes (butyric acid) will also develop. Under their action, the mushrooms acquire an unpleasant, rancid taste;
Rinse and scald the containers used for salting thoroughly. When salting, be sure to add salt. It gives not only taste, but also weakens the effect of oil-acid microbes, and enhances the preservative effects of lactic acid.
According to the quality of salting, the mushrooms are divided into 1 and 2 varieties, other types of mushrooms are not divided into varieties.
For salting, mushrooms, milk mushrooms, traps, chernushki, pigs, and whites are mainly used. You can also use porcini mushrooms, aspen and boletus. Before salting, previously peeled mushrooms are washed, soaked in water or blanched to remove bitterness and unpleasant odor. Mushrooms are salted in cold or hot ways.
In the cold method, the mushrooms are stacked with their hats down in barrels, 6-8cm layers, pour each layer with salt and spices (bay leaf, pepper, dill, currant leaves). Mushrooms should be covered with a layer of brine. If they are not covered with a layer of brine, then you can add a 5% salt solution, boiled and cooled. The top layer is sprinkled with salt more densely, covered with a clean napkin, a wooden circle with a stone-oppression is placed on it. When, after a few days, the mushrooms settle strongly, you can report the mushrooms salted separately. Excess pickle from mushrooms is collected and used for soups and sauces.
In the hot method, the washed mushrooms are boiled in slightly salted water (20-40 minutes), cooled and salted. Mushrooms are laid out in jars, add salt, a napkin and a load on top. Seasoning is placed at the bottom of the dishes or mixed with mushrooms. The brine should completely cover the mushrooms, if it is not enough, then prepare the brine from boiled water and 2 tablespoons of salt (50r). After 6-7 days, the mushrooms are suitable for consumption. A good flavor is obtained when garlic, horseradish, tarragon and dill stalks are added to the mushrooms
For salting, the mushrooms can be blanched and then salted as described above.
Mushrooms in all species have valuable nutritional properties. But some of them have more valuable properties (fresh mushrooms) compared to others (canned, salted, pickled). However, this does not prevent them from having equivalent use in cooking.
3. Fermentation of mushrooms.
For pickling, it is better to use mushrooms with a fleshy fruit body - chanterelles, mushrooms, autumn mushrooms, etc. Mushrooms are soaked for 5-6 hours, then allowed to drain. In the dishes, the mushrooms are transferred with blackcurrant leaves, dill stems, parsley, horseradish roots, garlic and sprinkled with salt. Then close with a napkin, stone oppression and leave for fermentation. After a few days, the mushrooms will settle, they should be completely covered with brine. Fermentation time is one to two months, depending on temperature. At the same time, bitterness, pungent taste disappears in the mushrooms and can be used as a side dish or snack. To speed up the process, add sugar or whey to the mushrooms.
4. Mushrooms in their own juice.
Small mushrooms are left intact, and large ones are cut into pieces. Warm up until juice and cook for 10-20min. with the addition of salt. They are laid out in jars, filled with mushroom broth, hermetically closed and quickly cooled, they must be stored in a chilled room. When stored in an apartment, put the mushrooms in jars and sterilize for one hour.
5. Fried mushrooms.
Prepared mushrooms are cut into slices. Heat the oil, put the mushrooms, add salt, cover with a lid and cook for 45–50 min with a slight boil, and then fry without a lid until the juice is removed from the mushrooms and the oil becomes clear. We shift into cans, fill with the remaining butter and close.
6. Mushroom extract
When small mushrooms are heated, a lot of juice is secreted, the mushrooms are boiled in their own juice for 30-40 minutes, filtered, added salt and steamed without a lid until the extract thickens. Poured into sterile dishes and corked.
7. Drying of mushrooms.
Drying is the most common way to process mushrooms. In the process of drying, the mushrooms acquire a characteristic aroma. Porcini mushrooms are divided into three commercial grades by quality: 1st, 2nd, 3rd. The remaining dried mushrooms are not divided into varieties.
Young, fresh mushrooms are dried. Porcini mushrooms, brown boletus, boletus, chanterelles are especially tasty. In large mushrooms, a leg is cut off, young ones are dried whole. Mushrooms are cleaned from needles, leaves and laid (for drying) on \u200b\u200ba wire rack or with a thin layer on a baking sheet in an oven, or on a stove at a temperature of 90-95 ° C. You can string the mushrooms and dry them in the sun or attic. mushrooms are dried until they become elastic and not brittle. Porcini mushrooms, chanterelles and parasol mushrooms in the dried form are light, boletus, boletus are dark. Dried mushrooms are stored in a dry room in a closed container.
8. Mushroom powder
Mushroom powder can be prepared from various edible mushrooms. It is best to use mushrooms with a pronounced aroma - mushrooms, mushrooms, umbrellas, ordinary lines, etc.
Mushrooms are dried in slices to hardness and crushed, sieved, separating small fractions, which are more easily dissolved. Keep the powder in an airtight container. Before use, the powder is mixed with warm water and allowed to swell for 20-30 min. and boil for 10-15 minutes. Mushroom powder is a good seasoning for soups, sauces and main dishes of meat, vegetables.
10. From the mushrooms you can cook many dishes. Their assortment is very large. Dishes from mushrooms not only diversify human food, but also bring into the body a certain proportion of the nutrients necessary for normal human life. From the entire range of existing mushroom dishes, the following most common dishes in public catering can be offered.
With mushrooms, you can cook vegetable, meat, cereals, legumes, flour dishes, etc. Mushroom sauces are widely used for boiled cold or hot, as well as fried meat.
Fried or stewed mushrooms can be garnished with dishes of poultry, young meat, young boiled potatoes.
Table 4.
Food group | Range |
Cold and hot dishes and snacks. | Hot sandwiches with champignons, salted mushroom caviar, pickled mushroom salads, mushroom stuffed eggs, mushroom stuffed tomatoes, mushroom and herring minced meat, mushroom oil, mushrooms baked with cheese, ham, fish, etc. |
First meal | Dried mushroom broth, mushroom hodgepodge, chanterelle soup, cabbage and sauerkraut soup, cabbage with mushrooms, noodle soup with mushrooms, vegetable soups with mushrooms, mushroom soup with cereal, with dumplings, with egg, borsch with mushrooms, mushroom soup puree, etc. |
Second course | Fried mushrooms in sour cream, mushroom cutlets, stewed mushrooms, baked champignons, mushrooms in the estimate, fried mushrooms hats, stewed cabbage with mushrooms, stewed mushrooms, fish in a sauce with mushrooms, fried and stewed meat with mushrooms |
Mushroom sauce, mushroom sauce with vegetables. sauce with mustard and horseradish, lemon sauce. champignon sauce with wine and cream, mushroom sauce with tomatoes, mushroom sauce with dry wine, tomato sauce with mushrooms and celery, with dill, sour cream, etc. |
|
Confectionery | Pie with mushrooms, pies with minced mushrooms, kulebyak with mushrooms, baskets with mushrooms and crayfish. casserole of bread and mushrooms, etc. |
Mushroom jelly.
Fresh mushrooms are boiled and chopped, the dry ones are soaked, boiled and chopped, the salted ones are soaked from brine, washed and cut.
The gelatin is soaked in water and, when heated, dissolved in a decoction of fresh mushrooms with the addition of salt and garlic. For jelly from pickled mushrooms, gelatin is dissolved in water with the addition of brine or marinade. The crushed mushrooms are covered with dissolved gelatin in molds or dishes and cooled.
You can serve garlic sauce to it: boiled egg yolks are ground with salt, mustard and sugar, pour in vegetable oil, diluted with vinegar or kvass. Add chopped parsley and dill, mashed garlic.
Caviar from salted and pickled mushrooms.
Mushrooms are washed, filtered and finely chopped. Finely chop the onion, lightly fry in vegetable oil and cool. Mushrooms are combined with onions, add black pepper and mix well. Put the finished caviar on a plate, sprinkle with herbs.
Sandwiches with champignons.
Cut fried champignons, mix with lemon juice, oil, salt and ground pepper. Grate the bread on one side with garlic, fry in oil and lay the mass with mushrooms, decorate with lettuce, chopped egg and herbs.
Smoked eel with champignon salad.
Peel and chop the mushrooms into thin slices, pickle the onions and chop finely. Mix cottage cheese with vegetable oil, ketchup, pepper, sugar and vinegar, grated apple. Put the mass on slices of bread with eel and arrange with lettuce.
Chanterelle salad.
Boil the chanterelles in salted water with the addition of thyme (2-3 branches), cool, basil leaves, anchovy fillet, chop the garlic and add lemon juice. Grind the egg yolk, beat with vegetable oil and mix with basil, chanterelles and let stand 30 minutes. When serving, put in a slide, sprinkle with parsley, arrange with croutons of white bread and whipped butter.
Jellied of chanterelles with game.
Chanterelles cut into 4-8 parts, chop the flesh of game and carrots into cubes, pour sherry, cognac, lemon juice, add parsley, keep in the cold. Prepare jelly from sherry, pour into molds and let it harden to make a “shirt”, put jelly on lettuce leaves and slices of truffles, put salad on top and fill in the remaining jelly, let it freeze in the refrigerator. When serving, dip the mold in hot water for 15-20 seconds, put on a dish and arrange the aspic with lemon and herbs.
Spicy champignons.
Carrots, cabbage celery, chopped onions in small cubes or chop. Peel the mushrooms, separate the legs from the hats, cut large ones into pieces. Prepare the marinade from the water. vinegar, sugar, pepper, bay leaf, pour them mushrooms with vegetables, add garlic, sprigs of dill and sterilize for an hour, close hermetically.
Dried mushroom broth.
Mushrooms are cooked on low heat for 20-30 minutes, then add onion and roots cut in half, salt and cook until cooked. Squeeze the broth from the fire and let stand, filter. Mushrooms and roots are cut into strips and mixed with herbs. The mixture is put on a plate and poured into broth.
Mushroom solyanka.
Boil dried mushrooms, strain and cut into strips. Chop the onion and fry with mashed tomato in butter. Cut pickles into slices. Prepared foods are introduced into boiling broth and cook for 10-15 minutes. Then put the mushrooms, peppercorns, bay leaf, salt and let it boil. Add pitted olives, capers and cook for 5 minutes. Pour the prepared hodgepodge into plates, put sour cream, a circle of lemon and sprinkle with herbs.
Fried mushrooms with onion gravy.
Salt whole young mushrooms, sprinkle with pepper and fry in vegetable oil for 25-30 minutes. Then remove from heat and leave in a warm place. Chop the onion, fry in oil, add sour cream, salt and bring to low heat over low heat. Ready sauce pour mushrooms and garnish with herbs.
Stewed mushrooms.
Dice fresh mushrooms, put in a saucepan and salt. To them add chopped and fried onions, pour water and simmer for 25-30 minutes. Then season the mushrooms with passivated flour and sour cream, bring to a boil.
11. The above material confirms the provision on the benefits and taste of mushrooms, on the possibility of their use in nutrition, expanding the range of dishes with their use.
However, mushrooms not only perform these functions, but are often used in medicine. People have long known the properties of molds - kill pathogenic microbes or delay their growth and development - antibiotics that are obtained from molds. In folk medicine, there are various recommendations for the use of mushrooms. So. frost-bitten areas of the body are treated with porcini mushrooms, the alkaloid Herzenin is found in them, which is recommended for angina pectoris, as well as to increase the vitality of the body. Oils in the resinous substance contain components that have an effect on headaches, gout and other diseases.
Veselka ordinary after drying is used to obtain aqueous and alcoholic solutions, which are recommended for gastrointestinal diseases and for wound healing.
Red fly agaric has the glory of a poisonous mushroom, because contains muscarine and muscaridin, as well as the antibiotic muscarufin, which in small doses enhances the activity of the endocrine glands and thereby increases the tone of the body. This mushroom is used for neuralgia, headaches, atherosclerosis, in various sets of homeopaths. Sick animals eat it in the woods.
The most poisonous and dangerous mushroom - pale toadstool is used for cholera diseases, and ordinary honey agaric as a mild laxative.
Red mushroom mushroom has special properties. It belongs to the group of edibles, it is used for cooking, frying, stewing and in this state it is edible. But it contains toxic substances that do not dissolve in water in the preparation of dishes, nor in the stomach and intestines during the digestion of food, but they dissolve in alcohol. And then the poisons enter the bloodstream and after 1 ... 2 hours all the signs of poisoning appear: nausea, vomiting, palpitations, the body takes on a red-violet hue. With small doses of poison, the patient recovers in 20 ... 24 hours, but with alcohol again, all signs of poisoning may return.
Of particular interest in medicine is the fungus “chaga” or “cancer” of birch. It grows in the form of a black outgrowth of irregular shape weighing 0.5 ... 2 kg in places of violation of the integrity of the tree bark.
Since ancient times, chaga has been used as an aqueous infusion for the prevention of gastrointestinal diseases and malignant tumors. The medicine from chaga noticeably improves the general condition of patients, delays the growth of tumors and the development of metastases. Its use gives positive results in the treatment of cancer and diseases of the digestive system.
Mushroom cartilage-milkman is used for urolithiasis as a diuretic. In saffron milk found an antibiotic substance - lactariviamine. An extract from field champignon delays the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, as well as typhoid and paratyphoid pathogens.
In the giant white clitocybe, there is the antibiotic clitocybin, which inhibits the growth and development of bacteria, as well as tuberculosis pathogens.
Various types of raincoats are used by people to stop bleeding, with kidney disease, and to fight tumors. An extract from the summer honey open significantly stops the development of microflora, delays mold.
The garlic mushroom is a source of bactericidal substances, it does not rot, helps preserve the components of food, and increases its shelf life.
Study work healing properties fungi continues in many countries and can be thought. That new properties of mushrooms will be discovered in the struggle for human health.
12. The oyster mushroom ordinary belongs to nadrevny saprotrophs. In recent decades, its cultivation has become widespread in different countries of Europe and North America.
Oyster mushroom can be grown throughout the year in special cultivation rooms on a cheap substrate.
For cultivation, a cellulose medium containing straw, corn cobs, sawdust, bran and other materials is used.
In France, the Bordeaux research station has been successfully used as a substrate for growing oyster mushrooms in the bark of trees and urban waste. Oyster mushroom can grow on trunks deciduous trees (poplar, willow, hornbeam, beech, oak).
For catering, interest may be the cultivation of oyster mushrooms in the basement, under controlled conditions.
The method of intensive cultivation of oyster mushroom was developed by Hungarian scientists and substantially improved by our researchers. In Germany, special industrial plants have been developed and are successfully used for the continuous preparation of a substrate intended for the cultivation of oyster mushrooms.
In our country, work on the cultivation of this fungus by industrial methods was carried out in 1975 (That K Oyster mushrooms on the conveyor. Science and Life, 1975, No. 5). The industrial cultivation of oyster mushrooms is devoted to the work of Dudki I.A., Shepy V.V., Yakovenko 0.3., Baccepa S.P. and others (1976, 1978, 1980).
Until now, the cultivation of this fungus has not been widely distributed in our country. But recently, due to a sharp decrease in mushroom picking in natural conditions due to environmental pollution, interest in cultivating oyster mushrooms has increased significantly. Growing oyster mushrooms in closed rooms allows you to get a product that is safe in its content of substances harmful to humans: without radioactive substances and pesticides.
The chemical composition of oyster mushroom.
The work of the Kiev Institute of Botany of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine dedicated to the study of the nutritional and biological value of oyster mushroom processing products (mushroom powder from common oyster mushroom mycelium) N.G. Cold and HIOP. The results of N.V. Dudenko, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor E.F. Solomko, candidate of biological sciences (1989) showed that mushroom powder of dried oyster mushroom middel is a source of biologically valuable protein, fat, fiber, micro and macro elements.
Bacteriological studies carried out by these scientists did not detect pathogenic microorganisms in the test materials. Data on the digestibility of mushroom powder and relative biological value indicate that its proteins belong to biologically valuable proteins.
The chemical composition of oyster mushroom
Research Ponomareva P.F., Kaltunova B.P., 1989. They showed the possibility of storing and transporting the cultivated oyster mushroom fungus in packages of polymeric materials.
The use of oyster mushrooms in cooking is poorly understood. Employees of the Lviv Trade and Economic Institute P.F. Ponomarev and B.P. Koltunov (1989) studied the quality (taste, aroma) of salted and pickled oyster mushrooms. It is noted that pickled oyster mushroom gave excellent results (taste and aroma - 5 points, texture - 4.94 points).
The organoleptic characteristics of mushroom caviar from hats and oyster mushroom legs were studied. Separate processing of hats and oyster mushroom legs for mushroom caviar is caused by higher stiffness of the legs, which significantly influenced the quality of mushroom caviar as a whole.
Assessment of the taste of caviar from oyster mushroom legs was slightly inferior to the taste of caviar from oyster mushroom hats. To improve the consistency of mushroom caviar from oyster mushroom legs, the authors recommend using grinders with smaller hole diameters to grind the legs. Various editions of cookbooks contain recipes for oyster mushrooms for home cooking. We did not meet data on the approved recipes for oyster mushrooms for catering.
We have studied the possibility of using oyster mushrooms directly for the production of culinary products in public catering establishments not in the distant future, but now. Before proceeding to the development of food recipes, at the first stage of our work, we determined the amount of waste during the mechanical processing of oyster mushrooms, the ratio of the mass of the legs and oyster mushrooms hats, and losses during heat treatment. We have not seen such data in the literature. There is information about the influence of conditions for the cultivation of oyster mushrooms on the ratio of the mass of legs and hats and the ways of directed increase in the mass of hats by creating certain modes in the process of growing mushrooms. However, there is no data on the quantitative ratio of the mass of legs and caps. Separate study of these parts is associated with their different rigidity, which allows us to conclude that it is necessary to develop various processing modes and production schemes for dishes from oyster mushroom legs and hats.
Processing and use of oyster mushroom.
We studied two varieties of oyster mushroom - Don and Florida, grown under the same conditions in the basement on a crushed substrate of wheat straw. It should be noted that oyster mushroom grown in these conditions requires minimal labor costs during machining. This is because there is no need to cut off the lower part of the leg, since it is not contaminated with earth. There is no need to repeatedly wash the mushroom caps from the ground and sand, since the mushroom growing conditions are such that the caps are not contaminated. The amount of waste for cleaning legs from traces of straw does not exceed 2.1%. The amount of waste in the varieties "Florida" and "Don" is almost the same (2 - 2.1%).
For comparison: when machined, champignons are formulated according to the 1981 collection of recipes. - 24%.
The mass of hats for oyster mushrooms of the Florida variety is 76%, and Don is 83%.
The mass of legs for oyster mushrooms of the Florida variety was 24%, and the variety Don was 17%.
The mass loss of these mushrooms when the whole hat with legs was turned up was 28%, the same for the “Phloid” and for the “Don”. For comparison: the loss of mass of champignons during stewing is 40%.
Losses in the mass of oyster mushrooms (caps with legs), sliced \u200b\u200bduring frying from raw, account for 40%. Weight loss is not dependent on the variety. For comparison: the mass loss of fried champignon from raw is 60% (sliced).
It was found that the mass loss of the hats during stocking is 17%, while frying - 21%. For legs, respectively 38% and 50%.
It should be noted that the intensity of the mushroom smell of oyster mushrooms after heat treatment compared with raw mushrooms increases significantly.
To compare the smell and the consistency of oyster mushrooms, which were cooked and roasted in comparison with champignons, we tasted the dish “mushrooms in sour cream sauce" "(rec. No. 369). These indicators were evaluated on a five-point system. The mushrooms were steamed, then cut into slices, poured with sour cream sauce, sautéed onions were added and boiled for 10 minutes.
A dish was also prepared, but the mushrooms were poured with boiling water, and then cut into slices and fried with onions. Then it was poured with sour cream sauce and boiled for 10 minutes.
13. Mushrooms have long been considered a valuable, high-protein and gourmet food product. Wild mushrooms. collected spontaneously cause a significant number of poisonings. Due to the high mortality, mushroom poisoning are on a par with the most dangerous diseases of nutritional origin. In 1996 poisoning by wild mushrooms in Ukraine acquired the character of an emergency during the period of fruiting of the mushrooms, about 3 thousand people were involved in the epidemic process, of which children accounted for 25.6%, that is, every fourth victim is a child. As a result of mushroom poisoning, 7.9% of the victims died, including among adults 7.7%, and among children 8.3%. Almost all mushroom poisoning was associated with unorganized collection.
In this light, the urgent need to put into practice a more effective system of measures for the prevention of mushroom poisoning with an emphasis on the prevention of diseases associated with unorganized collection becomes apparent.
One of the promising ways to improve the prevention of mushroom poisoning is the use of a paradigm based not on the method of system analysis and modeling.
Our proposed paradigm is a series of interconnected, interdependent links (Scheme 1).
The creation of a system of preventive measures is due to the corresponding reason - the possibility of substituting poisonous edible species of fungi and violating the rules for processing conditionally edible mushrooms. The proposed paradigm aims to create guarantees to prevent the use of poisonous mushrooms in writing and compliance with the rules for preliminary detoxification of edible and conditionally edible mushrooms. In the link “Cause” it is important to highlight the available etiofactors of fungal poisoning. Among poisonous mushrooms growing in Ukraine, only 1/9 - 1/10 of poisonous mushrooms have been registered as etiofactors in the last 25 years (pale grebe, false mushrooms, line, gray poisonous entomol, poisonous clitocybe, brownish-red lepiota).
The second and third links of the mushroom poisoning prevention paradigm are associated with the practical activities of health services, which aim to prevent the possibility of the threat of mushroom poisoning.
The paradigm of the prevention of mushroom poisoning.
Activities aimed at the personality of the mushroom picker: necessary knowledge |
|
distinctive features of edible and poisonous mushrooms | rules for the collection, storage, preparation (KKT-2) |
In the absence or presence, but not in full: The occurrence of food poisoning |
|
Improving the preparedness of treatment and care services in case of the threat of mushroom poisoning in growing season: |
|
cycle of lectures for health workers in the clinic, treatment and prevention | Workshops with paramedics medical care |
Prevention of fungal poisoning by health services: |
|
market control: Specially allocated places for sale, equipped with stands; Sale of mushrooms in accordance with the permitted list; Harvesting and selling only sorted by type of mushroom; Prohibition of the sale of dried agaric mushrooms; Prohibition of the sale of a mixture of mushrooms; | health education: In the media (television, radio, periodicals); Printed campaigning (brochures, memos, stands in crowded places, etc.) |
Note:
1. KKT-1 - critical control point - 1 (do not collect unknown mushrooms. Especially beware of mushrooms with a tuberous thickening at the base of the leg);
2. KKT-2 - a critical control point - 2 (do not pick mushrooms near transport highways and industrial enterprises, do not taste raw mushrooms, eat conditionally edible mushrooms after 2 times boiling, followed by removal of the broth).
Identification of the etiofactor of poisoning by poisonous mushrooms.
In cases of mushroom poisoning, the diagnosis “Mushroom poisoning” or “Poisoning with poisonous mushrooms" is most often diagnosed without mentioning the etiofactor - a type of mushroom. Identification of an etiofactor (a type of fungus) is crucial for the prevention of new similar poisonings and the provision of adequate medical care to a patient who has mushroom poison (poisons) in his body. The victims are usually provided with standardized medical care without taking into account the tropic effects of fungal toxins.
About 200 species of edible, more than 30 species of conditionally edible, about 70 species of non-edible and about 50 species of poisonous mushrooms grow in forests, forest belts and open spaces of Ukraine.
Most often, poisoning is caused by about 20 species of poisonous mushrooms.
Table 1.
Mushroom calendar of poisonous mushrooms
(fruiting periods, toxins, tropic effects).
Mushroom name | Fruiting time | Toxins, tropic action |
||
Hepato-nephrotropic |
||||
Inotsibe Patuyara | Neurotropic |
|||
Entoloma poisonous | September | Gastroenterotropic |
||
Champignon dark scaly | September | Gastroenterotropic |
||
Champignon-poisonous (yellow skin, tablet) | September | Gastroenterotropic |
||
Entoloma poisonous gray | September | Gastroenterotropic |
||
Pale grebe green | Hepato-nephrotropic |
|||
Yellow toadstool | Hepato-nephrotropic |
|||
White toadstool | Hepato-nephrotropic |
|||
Inotsiba striped | Neurotropic |
|||
Klitotsibe red-cotton poisonous | Neurotropic |
|||
Clitocybe Wax | Neurotropic |
|||
Amanita panther | Neurotropic |
|||
Poisoning is poisonous | Gastroenterotropic |
|||
Thin pig | Hemolytic |
|||
Amanita muscaria | Neurotropic |
|||
False honey agaric | Gastroenterotropic |
|||
Cobweb orange-red | September | Hepatropic |
||
Mushroom Kirk-sulfur-red umbrella | September | Hepatropic |
||
Mushroom umbrella korich-nevo - cherry | September | Hepatropic |
||
False honey agaric brick red | September | Gastroenterotropic |
||
Clitocybe is whitish | September | Neurotropic |
From table 1 it is seen that the fruiting of poisonous mushrooms begins in early spring (April) and ends in late autumn (November), that is, in all periods of growth of edible mushrooms. Consequently, the substitution of an edible mushroom by a poisonous one can occur during all periods of the vegetation of edible mushrooms.
The first poisonous mushrooms (lines) appear in April. In May, champignons (dark-scaly and poisonous) and Patuyara nnociba join them. In the first month of summer (June) the fruiting of many poisonous mushrooms begins: pale grebe (green, yellow. White), poisonous gray entoloma, striped inotsiba, clitocybe (reddish poisonous and waxy), and panther fly agaric.
In the last month of summer (August), new species of poisonous mushrooms appear: poisonous mushroom poisonous mushroom false sulfur-yellow, fly agaric. In the first month of autumn (September), many other poisonous mushrooms begin to grow: the cobweb is orange-red, the fungus is an umbrella (brown-gray-red, brown-cherry), the honey agaric is false brick red clitocybe whitish. The time of the appearance of poisonous mushrooms ends in the autumn months. The exception is lines (spring mushrooms).
Knowing the timing of the appearance of poisonous mushrooms and the tropic effect of mushroom toxins (clinic), it is easier to identify the etiofactor of mushroom poisoning - a type of poisonous mushroom in the process of investigating diseases that have arisen.
In case of poisoning with gastroenterotropic poisonous mushrooms (poisonous entoloma, dark-scaled champignon, poisonous champignon, poisonous gray entoloma, poisonous rowad, false sulfur-yellow shell, false brick red honey agaric), the latent period is 1 / 2-2 hours, the main symptoms are observed side of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenteritis). The autonomic nervous system is rarely affected (sweating). There are no signs of damage to other organs (liver and kidneys) and systems (central nervous system).
In case of poisoning with neurotropic poisonous mushrooms (Patuillard inocibus, striped inotsiba, red clitocyte poisonous, waxy clitocybe, whitish clitocybe, panther fly agaric, red fly agaric), symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract are affected (gastroenteritis), vegetative vegetation, abundant separation from the nose, narrowing of the pupils, bradycardia: with a predominant content of muscardine in the mushrooms - dilated pupils and tachycardia) and the central nervous system (spinal consciousness, agitation, delirium, hallucinations, seizures). Symptoms of liver and kidney damage are absent. The latent period is 1/2 - 2 hours, that is, the same as in case of poisoning with gastroenterotropic poisonous mushrooms.
Poisoning with hepato-nephrotropic poisonous mushrooms (pale toadstool green, pale toadstool yellow, pale toadstool white, stitches, cobweb orange-red, brown-cherry umbrella mushroom) are accompanied by gastroenterocolitis with dehydration and desalination of the body. In case of poisoning, lines of diarrhea may not be, and cobwebs - constipation is noted. Symptoms of a lesion of the ANS are absent, but violations of the central nervous system are pronounced - loss of consciousness, convulsions, coma. Symptoms of damage to the liver (hepatitis) and kidneys (nephroso-nephritis) are characteristic - to their acute failure. The latent period is from 3 to 48 hours, with poisoning by a cobweb, from 2 to 17 days.
At the clinic, you can only tentatively judge the etiofactor of mushroom poisoning. An accurate diagnosis with the establishment of the type of poisonous fungus that caused poisoning can be made only on the basis of mycological studies of fungi or their remains.
Among poisoning with poisonous mushrooms, poisoning with a toadstool prevails (about 30%). Distinctive mycological features are shown in table 2.
Confirm the belonging of the mushrooms to the amanital group (pale toadstool), which caused poisoning, by the following research methods (I.P. Shlopak, O.I. Tsiganenko, 1996):
1. Guaiacol. 1-hydroxy-2-methoxybenzene or hydroxyanisole. With a positive reaction, a bluish-greenish, bluish-grayish color of the pulp of the fungus is noted.
2. 10% aqueous solution of ferric chloride. With a positive reaction, the pulp of the fungus turns greenish, and then dark gray.
3. Dissolve 1 g of iron sulfate in 10 ml of distilled water with the addition of 2-3 drops of sulfuric acid. With a positive reaction, the flesh of the mushroom is stained in olive, light green, orange, brown.
Table 2.
Distinctive mycological signs of pale toadstool from
edible mushrooms (according to S.A. Kuzmenko, A.I. Lokay, A.Ya. Popovich, 1976).
Records | Spore powder |
||||
Death cap | Greenish, yellowish, white, flakes on it are often absent. | Before old age, white | White with a very delicate ringlet; down tuberoid collar | White color |
|
Champignon | White or brownish, flakes are always absent. | Pale pink, then dark brown | White with a dense ring, without tuberous thickening and a collar. | White, turning pink | Black and brown |
Russula | Greenish, yellowish, white, flakes are always absent. | White, rarely light yellow | White without ring, without tuberoid thickening and collar. | White, fragile | White color |
Annular cap | Yellowish, with a whitish powdery coating on the hat. | Light clay Later rusty brown. | White with captive ring. At the bottom of the gate is a nickname, often absent. Without tuberous thickening | Just white | |
Brownish-yellowish, olive brown without cereal. | Gray-yellow color. | Grayish - yellow in color, without ringlet and tuberoid thickening. | White or slightly yellow | White color |
Rules for the Detoxification of Conditionally Edible and edible mushrooms.
In the raw fruit bodies of many species of edible mushrooms, toxic substances have been found. In some cases, these substances are found in such valuable edible fungi as porcini mushroom and chanterelle.
Undercooked or undercooked mushrooms can cause poisoning. Since the toxic substances found in edible mushrooms are non-heat-resistant, before cooking, edible mushrooms must be subjected to preliminary boiling and washing in running water.
The quality of edible mushrooms is very significantly affected by “acid” rains. The potential danger of consuming such mushrooms can be reduced by pre-soaking and boiling, followed by washing in running water.
Edible mushrooms growing near highways and industrial enterprises may contain toxic elements - lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic, etc. Therefore, it is not recommended to collect mushrooms near transport highways and industrial enterprises.
Many conditionally edible mushrooms are included in the standards for mushroom products: honey agaric. felts, thrills, bitter bitter mustard, morel common, morel, conic morel, morel cap, etc. Cooking dishes from conditionally edible mushrooms is possible only after detoxification by 2-fold (20 min.) boiling them cut into pieces, and then washing in running water.
Rapid assessment of the toxic properties of fungi.
Tests are carried out on two types of laboratory animals: white male mice with a body weight of about 20 g and white male rats with a body weight of 90-110 g.
For the study, samples of mushrooms of the same species are taken (if possible); optimal sample weight - 1 kg. All mushrooms must be whole, intact, thoroughly cleaned of debris and earth. Before the start of research, mushrooms can be stored in the refrigerator for no more than one day at temperatures up to + 6 C, for several days - when stored in the freezer.
Setting up a bioassay.
A sample of fresh (freshly frozen) mushrooms is ground in a laboratory mill or meat grinder. Two laboratory samples of 10 g each are taken from crushed and well-mixed mushrooms for the preparation of homogenates intended for administration to laboratory animals:
a) for research on mice: 40 ml of distilled water is added to 10 g of mushroom mass;
b) for research on rats: 10 ml of distilled water is added to 10 g of mushroom mass.
Each sample is thoroughly mixed and homogenized in a glass homogenizer - until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
To study each type of mushroom in the group must be at least 10 animals. The homogenate is administered once intragastrically by a probe at the rate of 5 g of mushrooms per 1 kg of body weight: 0.5 ml of homogenate “a” to mice weighing 20 g and 1 ml of homogenate “b” to rats weighing 100 g.
After a single injection, the animals are on a general bivalent diet, their condition is monitored for 10 days.
Production of an intraperitoneal test.
With the intraperitoneal method of introducing mushrooms, their sample is prepared as follows: 25% aqueous homogenate of fresh (freshly frozen) mushrooms (1 part of mushrooms and 3 parts of water) is divided into two parts, after which one of the parts is boiled for 15-20 minutes. The resulting homogenate is centrifuged and the supernatant is injected intraperitoneally with at least 6 animals at the rate of 0.1 ml per 10 g of animal weight (in terms of fresh weight of the fungus, the dose is 2.5 g / kg). The period of observation of animals is not less than 3 days.
Assessment of the results of the study: the absence of toxic effects allows us to make a preliminary conclusion about the possibility of eating these mushrooms in food. In the presence of a toxic effect, additional toxicological studies are necessary in order to identify a possible toxic agent with the involvement of biologists (botanists, phytopathologists). In the case of whitening animals, their autopsy is performed with histological examination internal organs: liver, kidneys with adrenal glands, intestines, heart, to determine the nature and capabilities of the ethnologists of the lesions.
Wrong (false) ideas about the ways
recognition of poisonous mushrooms.
A rather significant number of mushroom pickers have erroneous ideas about the so-called simple ways of recognizing edible and poisonous mushrooms. The following are some of the methods that are essentially dangerous delusions of mushroom pickers.
1. A silver spoon or a silver coin dipped in a decoction of mushrooms turns black if there are poisonous mushrooms in the pan. Darkening of silver objects depends on the chemical action of silver on amino acids containing sulfur, resulting in the formation of black and silver sulfide. Such amino acids are found in both edible and poisonous mushrooms.
2. 2. If the head of onion or garlic turns brown when cooked together with mushrooms, then among them are poisonous. Both poisonous and edible fungi can cause brown onions or garlic, depending on the presence of the tyrosinase enzyme in them.
3. Larvae of insects and snails do not eat poisonous mushrooms. Insect larvae and snails eat both edible and poisonous mushrooms.
4. Poisonous mushrooms must cause souring of milk. Souring of milk occurs under the influence of enzymes such as pepsin and organic acids, which can be found in both edible and poisonous mushrooms.
5. Poisonous mushrooms must necessarily have an unpleasant smell, in edible - pleasant. The smell of a deadly poisonous mushroom of a pale toadstool is no different from the smell of champignon.
6. All mushrooms at a young age are edible. Pale grebe is equally deadly poisonous in both young and adulthood.
Literature
1. Commodity research of food products. M., Economics, 1982-
2. Pipe 1.0., Wasser S.P. Mushrooms in nature and human life. Kiev, Naukova
dumka, 1980 - 166s.
3. Masso S., Relove O. Meat and mushroom dishes. Tallinn, Issue, 1984., -
4. Scientific report of the department. Rizrobka technologist vikoristannya u kharchuvannі
wild plants i low-fat vegetables, herbs, fruits and berries. Donetsk, 1996
5. Zerova M. Ya., Rozhenko G.P. Atlas of edible and poisonous mushrooms. Kiev,
"Radyanska school", 1988 - 40s.
6. Wasser S.P., Soldakova I.M. Higher basidiomycetes of the steppe zone
Ukraine. - Kiev: Naukova Dumka 1977 - 356s.
7. Food hygiene / Vanhanen V.D., Maystruk P.N., Stolmakova A.I. and etc/.
Kiev. Healthy "I, 1980 - 304s.
8. Prevention of mushroom poisoning. Methodical instructions. Donetsk
Many cap mushrooms are edible.
The most valuable of them are champignons, white, butterfish, aspen, boletus, mushrooms.
The formation of fruiting bodies in fungi of various species occurs at different times. As a rule, morels and lines appear first in late April - early May, then champignons.
In mid-June, when rye is earning, birch trees appear.
Following them - butterfish, boletus, russula. From the second half of summer until the first frosts, fruiting bodies form mushrooms of all kinds.
In dry weather, the fruiting bodies of the mushrooms begin to grow only at the end of summer, and when early cooling sets in, their growth stops.
When picking mushrooms, it is important to be able to distinguish edible mushrooms from poisonous ones!
Pay attention!
The most dangerous are pale grebe, fly agaric, gall mushroom, false chanterelles and false mushrooms.
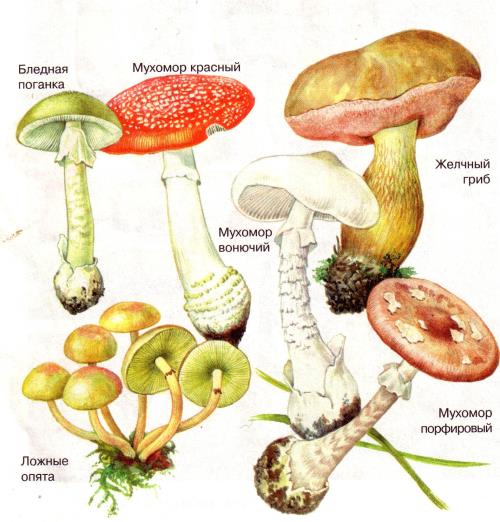
Pale toadstools similar to champignons, only the underside of the cap is greenish-white, unlike the pink in the champignon.
Fly agaric easy to recognize by a bright red hat with white spots. Fly agarics with gray hats are sometimes found.
Gall mushroom similar to white, but the upper part of its hemp is covered with a pattern in the form of a black or dark gray mesh, and the flesh on the break turns red.
False chanterelles they are similar to edible chanterelles, but their hats are smooth reddish-orange, and not light yellow like those of edible ones, and white juice stands out from the broken hat of the false chanterelle.
Edible mushrooms on a hemp have a film ring, and false mushrooms there is no such film and the plates under the hat are greenish.
Pay attention!
In order not to be poisoned by mushrooms, be careful when collecting them. If the mushroom found is similar to poisonous or you doubt its edibility, you better not take such a mushroom. Old fruiting bodies of edible mushrooms can also be poisonous. You cannot pick mushrooms near roads, chemical and other industrial enterprises that pollute the environment with harmful substances. The fruiting bodies of fungi accumulate these substances.
Mushroom cultivation
The fruiting bodies of many mushrooms contain nutrients that are beneficial to humans. Therefore, some cap mushrooms have long been cultivated in artificial conditions.
In vegetable farms in large cities of our country, champignons are grown. In special workshops, four-tier racks (shelves) are installed. On them in the nutritious soil planted mycelium. In the premises of the workshops, such temperature and humidity of the air and soil are maintained at which fruiting bodies grow rapidly. More than 20 kg of mushroom fruit bodies are removed from 1 m² of soil. Up to five harvests of mushrooms can be obtained per year.
