Unusual facts about mushrooms. Interesting facts about mushrooms
In the world there are about 2 million types of mushrooms, but only about 80 thousand are classified. There are approximately 6 species of mushrooms per plant species.
Quite a few species of fungi are predators (although in essence almost all of them are unfriendly and cause the death of many plants and animals). Predator mushrooms have special devices (growths) for catching insects. And there are species that, spraying their spores and falling into a victim, grow in it.
In fly agarics there is not so much poison, in order for its concentration to be fatal, you need to eat about 4 kg. But pale toadstool, yes, it is very poisonous that just one mushroom is enough to poison 4 people.
On average, each mushroom consists of approximately 90% of water (just like a human).
One of the largest mushrooms found is considered an object found in the USA in 1985 (Wisconsin), its weight was 140 kg.
Mushrooms are not plants, as was previously thought, since they lack chlorophyll, but at the same time, they are not animals because they do not have a stomach.
The largest mushroom lives in Oregon, USA, its area of \u200b\u200bmycelium is about 900 hectares and weighs several hundred tons.
$ 2500 per 1 kg of mushrooms, this is the most expensive variety of mushrooms - truffle.
One of the most interesting mushrooms is considered to be "Plasmodium" the fact is that he knows how to walk. The speed is really small, only about a meter in a few days, but still ... But he lives in central Russia, that is, our neighbor.
The mycelium grows very slowly, about 10-12 centimeters per year.
Ginger can be eaten raw.
The very first antibiotic in the world was derived from a fungus (penicillin).
Perhaps one of the rarest mushrooms is the "Devil's Cigar" (Chorioactis geaster) you can meet it in the central part of Texas (USA), as well as in separate parts of Japan. In addition, this is the only mushroom that makes a sound (whistle) when it releases spores.
Mushrooms were discovered in the reactor of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 2002, and they felt great. And even more, they needed radiation in order to live (like the sun to plants). In the composition of these fungi, melanin was found (an analogue of what protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation). In general, mushrooms are very tenacious and their places of growth can be very extreme (space, sulfuric acid, high pressure).
By some properties, mushrooms as products are closer to meat, and by some closer to plants.
In general, mushrooms are very interesting and we sometimes don’t think about where they can still exist, but they live next to us in the form of yeast, yeast for fermented milk products, mold, and several types of mushrooms live in the human body, though not all of them are safe for health.
Mushrooms are not plants or animals, but representatives of a special kingdom, which covers more than 100 thousand species, which include mushrooms, mold and yeast.
Mushrooms, unlike plants, need ready-made organic food for growth and reproduction. The green pigment chlorophyll allows plants to synthesize nutrients through the energy of sunlight. Mushrooms lack chlorophyll and therefore receive nutrients from plants and animals.
Mushroom variety

On Earth, there are more than 100 thousand species of mushrooms. Some, like yeast, consist of a single cell, but most fungi form numerous filaments (hyphae) called mycelium or mycelium. They grow inside the body, which serves as their source of food. Many fungi settle on plants or in the soil, where they help break down the tissues of dead plants and animals.
Mushroom propagation methods
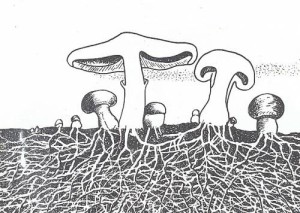
To reproduce, the fungi throw tiny spores into the air. Some mushrooms, in particular real mushrooms and toadstools, form large fruiting bodies that contribute to the spread of spores. Other mushrooms produce long threadlike stems with sporangia at the apex. Having landed in an auspicious place, the spore germinates, forming new mushrooms. Microscopic fungal spores surround us constantly.
Healthy mushrooms

Some mushrooms bring a lot of benefits: they contribute to the breakdown of the remains of dead plants and animals, serve as raw materials for the production of medicines, such as the penicillin antibiotic. Certain types of yeast are used to make bread and alcohol. There are also edible mushrooms, but sometimes it is extremely difficult to distinguish them from grebes containing deadly poison.
Harmful mushrooms
Mushrooms can grow on food waste, on paper, wooden buildings, and damp clothes. Fungal diseases harm and even kill plants, in particular cultivated ones, such as potatoes and strawberries. Some fungi bring a lot of trouble to people and animals, causing fungal diseases.
Tags: The use of mushrooms in medicine and the treatment of diseases, the useful and edible properties of mushrooms, interesting information for beginning mushroom pickers, the bad properties that can be found in the mushrooms you find, how they propagate and spread, which mushrooms can harm the health of an adult or a child.
Mushrooms(lat. Fungi or Mycota ) - the kingdom of wildlife, combining eukaryotic organisms that combine some of the signs of both plants and animals. Mushrooms are studied by the science of mycology, which is considered a branch of botany, since mushrooms were previously attributed to the plant kingdom.
The concept of mushrooms as a separate kingdom was formed in science by the 1970s, although E. Fries proposed to distinguish this kingdom in 1831, and Karl Linney expressed doubts about placing mushrooms in the plant kingdom in his “System of Nature”. In the second half of the 20th century, the idea of \u200b\u200bpolyphyletism of mushrooms was finally formed. Towards the end of the 20th century, data were accumulated on genetics, cytology, and biochemistry, which made it possible to divide this group of organisms into several branches unrelated to each other and distribute them between different kingdoms, leaving only one of them in the realm, or the actual mushrooms.
Thus, the scientific term “mushrooms” at the beginning of the 21st century became ambiguous. In the narrow sense of biological taxonomy, this is the name of a taxon, one of the kingdoms of wildlife. In the old, broader sense, the term has lost the meaning of a taxon and denotes an ecotrophic group that combines heterotrophic eukaryotes with a smotrophic type of nutrition. According to historical tradition, such organisms continue to be studied by mycology.
The biological and ecological diversity of fungi is very great. This is one of the largest and most diverse groups of living organisms, which has become an integral part of all aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. According to modern estimates, there are from 100 to 250 thousand, and according to some estimates, up to 1.5 million species of mushrooms on Earth. As of 2008 in the kingdom Fungi 36 classes, 140 orders, 560 families, 8283 generic names used and 5101 generic synonym, 97 861 species are described.
The role of mushrooms in nature and in the human economy is difficult to overestimate. Mushrooms are present in all biological niches - in water and on land, in soil and on all kinds of other substrates. Being reducers, they play an important role in the ecology of the entire biosphere, decomposing all kinds of organic materials and contributing to the formation of fertile soils. The role of mushrooms as participants in mutually beneficial symbiotic (mutualistic) communities is great. The symbiotic relationships of fungi with higher plants are known - mycorrhiza, with algae and cyanobacteria - lichens, with insects, representatives of the neocallimastigian order - an essential component of the digestive system of ruminants and some other herbivorous mammals, they play an important role in the digestion of plant foods.
Many types of mushrooms are actively used by humans for food, household and medical purposes. Edible mushroom dishes are traditionally included in the national cuisines of many peoples of the world. Many countries have developed the industrial cultivation of edible mushrooms, the production of materials for amateur mushroom growers. Microscopic mushrooms are used in the food industry for the preparation of drinks by fermentation, fermentation of various food products. Mushrooms are one of the most important objects of biotechnology used for the production of antibiotics and other medicines, some chemicals used in the food industry and for technical purposes.
On the other hand, mushrooms can cause significant harm. Phytopathogenic fungi, which are usually harmless in undisturbed natural ecosystems, can cause epiphytotics in agricultural plantations (agrocenoses), tree plantations, and in forests where economic activities are carried out. In animals and humans, fungi cause skin diseases (dermatomycoses), and sometimes damage to internal organs (deep mycoses). Very dangerous and can lead to fatal poisoning by poisonous mushrooms, as well as mycotoxicosis - food poisoning infected with toxins of microscopic fungi. Significant damage is caused by spoilage caused by fungi of various products and materials (biocorrosion).
